The Open Group OGEA-101 TOGAF Enterprise Architecture Part 1 Exam Practice Test
In which part of the ADM cycle do building block gaps become associated with work packages that will address the gaps?
Answer : D
In Phase E of the ADM cycle, building block gaps become associated with work packages that will address the gaps. This phase involves creating an Implementation and Migration Plan that defines a set of work packages and Transition Architectures that will deliver the Target Architecture. Reference: The TOGAF Standard | The Open Group Website, Section 3.2.5 Phase E: Opportunities & Solutions.
Complete the sentence A set of architecture principles that cover every situation perceived meets the recommended criteria of_______________
Answer : D
A set of architecture principles that cover every situation perceived meets the recommended criteria of completeness. Completeness is one of the six criteria that should be applied when developing or assessing architecture principles. Completeness means that there are no gaps or overlaps in the coverage of principles across all relevant aspects of the enterprise's architecture. Reference: The TOGAF Standard | The Open Group Website, Section 3.3.7 Architecture Principles.
Complete the sentence The TOGAF standard covers the development of four architecture domains. Business. Data, Technology and__________________.
Answer : D
The TOGAF standard covers the development of four architecture domains: Business, Data, Technology and Application. These domains represent different aspects of an enterprise's architecture and provide a consistent way of describing, analyzing, and designing them. Reference: The TOGAF Standard | The Open Group Website, Section 2.2 Architecture Development Method (ADM).
Consider the following chart:
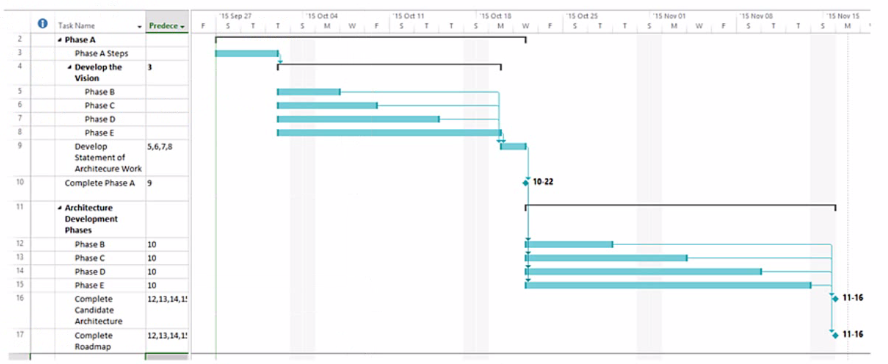
Which important concept for Enterprise Architecture Practitioners does it illustrate?
Answer : C
The chart shown is a Gantt chart, which is commonly used for project management to illustrate a project schedule. In the context of TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework), which is a framework for enterprise architecture, this Gantt chart is demonstrating the sequenced approach to the Architecture Development Method (ADM). The ADM is the core process of TOGAF which provides a tested and repeatable process for developing architectures. The ADM is described as being iterative, over the whole process, between phases, and within phases. For each iteration of the ADM, a fresh decision must be taken about each of the parameters (scope, granularity, time period, and architecture assets).
The ADM consists of a number of phases that have to be followed in sequence:
Preliminary Phase: Framework and principles
Phase A: Architecture Vision
Phase B: Business Architecture
Phase C: Information Systems Architectures, including Data and Application Architectures
Phase D: Technology Architecture
Phase E: Opportunities and Solutions
Phase F: Migration Planning
Phase G: Implementation Governance
Phase H: Architecture Change Management
Requirements Management
Each phase is dependent on the outputs of the previous phase and the Requirements Management phase runs throughout. The Gantt chart clearly shows the dependency and sequence in which these phases occur, implying that a structured approach is followed to produce the enterprise architecture.
The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2, a standard of The Open Group
What are the four dimensions used to scope an architecture?
Answer : C
These four dimensions help define the scope and boundaries of the architecture and ensure that it meets the needs and expectations of the stakeholders.
Which statement about Requirements Management is most correct?
Answer : D
This statement about Requirements Management is most correct because it reflects the central role of Requirements Management and stakeholder engagement in the ADM cycle. Requirements Management is not a step of all ADM Phases, but rather an ongoing process that ensures that all relevant requirements are elicited, analyzed, prioritized, and addressed throughout the architecture development and transition. Stakeholder engagement is also a continuous activity that involves identifying, communicating, and managing stakeholder expectations and concerns. Reference: The TOGAF Standard | The Open Group Website, Section 3.1 Introduction to the ADM.
Which of the following is included as part of Architecture Governance1?
Answer : A
Ensuring compliance with internal and external standards and regulatory obligations is one of the activities included as part of Architecture Governance. Architecture Governance is the practice and orientation by which enterprise architectures and other architectures are managed and controlled at an enterprise-wide level. It involves establishing processes, roles, responsibilities, policies, and standards to ensure that architectures are aligned with the enterprise's strategy and objectives, and meet the quality and performance requirements. Reference: The TOGAF Standard | The Open Group Website, Section 3.3.6 Architecture Governance.