The Open Group TOGAF Business Architecture Foundation OGBA-101 Exam Practice Test
Which ADM phase focuses on defining the problem to be solved, identifying the stakeholders, their concerns, and requirements?
Answer : A
In the TOGAF ADM (Architecture Development Method), Phase A, also known as the Architecture Vision phase, is critical for defining the problem to be solved and identifying the stakeholders, their concerns, and requirements. Here's a detailed explanation:
Phase A: Architecture Vision:
Objective: The primary objective of Phase A is to establish a high-level vision of the architecture project. This includes defining the scope, identifying stakeholders, and understanding their concerns and requirements.
Stakeholder Identification: During this phase, all relevant stakeholders are identified. This includes business leaders, IT leaders, end-users, and other parties who have a vested interest in the architecture project.
Concerns and Requirements: Once stakeholders are identified, their concerns and requirements are gathered. This involves understanding their needs, expectations, and the issues they face that the architecture project aims to address.
Key Activities:
Problem Definition: Phase A focuses on clearly defining the problem or opportunity that the architecture project seeks to address. This sets the stage for developing the architecture vision and ensuring that the project aligns with business goals.
Developing the Architecture Vision: A key output of Phase A is the architecture vision, which provides a high-level overview of the desired future state. This vision is aligned with the business strategy and objectives.
Requirements Management: Phase A also involves establishing a requirements management process to ensure that stakeholder needs are captured, analyzed, and addressed throughout the architecture development process.
TOGAF Reference:
Phase A Deliverables: Key deliverables of Phase A include the Architecture Vision document, stakeholder map, and high-level requirements.
ADM Guidelines and Techniques: TOGAF provides guidelines and techniques for effectively conducting Phase A, including methods for stakeholder analysis, requirements gathering, and developing the architecture vision.
In summary, Phase A of the TOGAF ADM focuses on defining the problem to be solved, identifying stakeholders, understanding their concerns and requirements, and developing a high-level architecture vision that aligns with business objectives.
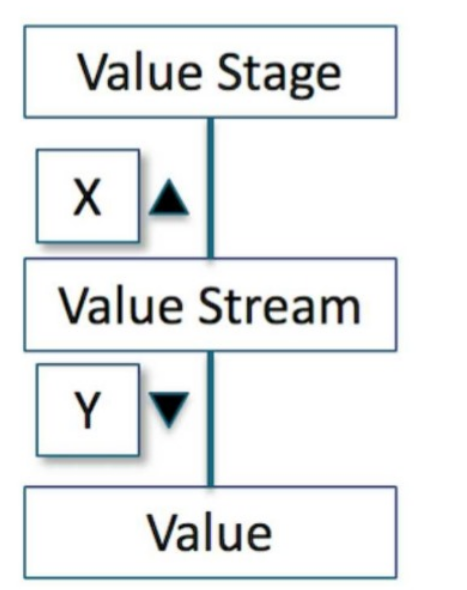
Consider the following extract of a model showing relationships between Business Architecture concepts:
Answer : B
In the context of TOGAF and Business Architecture, the diagram depicts the relationship between a Value Stream, Value Stage, and Value.
Value Stream: Represents the end-to-end set of activities that create and deliver value to a stakeholder.
Value Stage: A distinct step or phase within the Value Stream.
Value: The benefit delivered to the stakeholder.
The relationship 'X' indicates that a Value Stream is composed of multiple Value Stages.
Think of it like a journey (Value Stream) with multiple stops along the way (Value Stages). Each stage contributes to the overall value delivered at the end of the journey.
Refer to the table below:
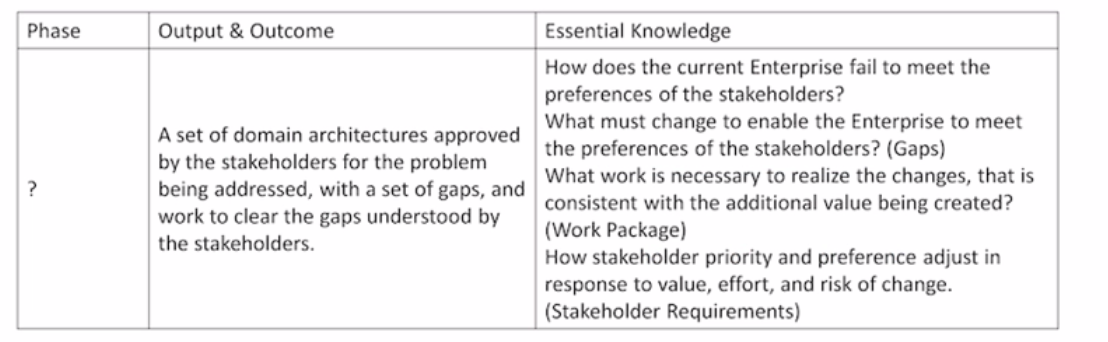
Which ADM Phase(s) does this describe?
Answer : C
The table describes the iterative cycle of defining requirements, identifying gaps, and creating solutions that occurs throughout the architecture development phases of the TOGAF ADM. This cycle is most prominent in:
Phase B (Business Architecture):
Develop the Business Architecture, identifying gaps between the baseline and desired business capabilities, processes, and information flows.
Define work packages to address these gaps and realize the target business architecture.
Phase C (Information Systems Architectures):
Develop the Data and Application Architectures to support the Business Architecture.
Identify gaps between the baseline and target information systems architectures.
Define work packages to address these gaps and realize the target data and application architectures.
Phase D (Technology Architecture):
Develop the Technology Architecture to support the Data and Application Architectures.
Identify gaps between the baseline and target technology architectures.
Define work packages to address these gaps and realize the target technology architecture.
Which of the following is the element of a value stream stage that describes the end state condition denoting the completion of the value stream stage?
Answer : D
In the context of a value stream within TOGAF, a value stream stage represents a segment of the overall process that delivers value to stakeholders. Each stage has specific characteristics and elements that help define its progress and completion. The 'exit criteria' is a key element that describes the end state condition, denoting the completion of a value stream stage. Here's how TOGAF defines and uses these concepts:
Value Stream Definition:
A value stream represents an end-to-end collection of activities that create a result for a customer, stakeholder, or end-user. It provides a visual representation of how value is delivered.
Value Stream Stages:
Each value stream consists of multiple stages, each contributing to the overall value delivery. These stages need to be clearly defined to ensure the value stream can be effectively managed and improved.
Exit Criteria:
Definition: Exit criteria are the conditions that must be met to signify the completion of a value stream stage. These criteria ensure that all necessary tasks have been completed and that the output meets the required quality and performance standards.
Purpose: By defining exit criteria, organizations can ensure that each stage of the value stream is completed before moving to the next, maintaining quality and consistency across the process.
TOGAF Reference:
Phase B: Business Architecture: In this phase, value streams and their stages are modeled. Defining exit criteria for each stage helps in managing transitions and ensuring that each part of the value stream is delivering the intended value.
In summary, the exit criteria define the end state condition of a value stream stage, ensuring that all necessary tasks are completed and quality standards are met before proceeding to the next stage.
Which of the following best describes information mapping?
Answer : A
Information mapping in TOGAF is a technique used to represent business information assets that are either currently in use or planned for future use by the enterprise. Here's a detailed explanation:
Purpose of Information Mapping:
Information mapping provides a clear visualization of how information flows within the enterprise, highlighting the information assets and their interactions. This is crucial for understanding the current state and planning the future state of information management.
TOGAF Framework:
Phase C: Information Systems Architectures: Within this phase, information mapping is used to develop the Data Architecture, which outlines the structure of an organization's logical and physical data assets and data management resources.
Supporting Analysis: Information mapping supports various analyses, including gap analysis, impact analysis, and the identification of information dependencies and redundancies.
Benefits:
Clear Representation: It provides a clear and structured representation of business information assets, aiding in the understanding and management of information flows.
Alignment with Business Processes: Helps ensure that information assets are aligned with business processes and objectives, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of information usage.
Components:
Current Information Assets: Information mapping identifies and catalogs the information assets currently in use within the enterprise.
Planned Information Assets: It also includes planned information assets that will be needed to support future business processes and strategies.
In summary, information mapping is a technique to represent business information assets in use or planned by the enterprise, providing a structured view of information flows and supporting effective information management.
Please consider the following statement.
They govern the architecture process, affecting the development, maintenance, and use of the Enterprise Architecture.
What does this describe?
Answer : A
Architecture Principles in TOGAF govern the architecture process, influencing the development, maintenance, and use of the Enterprise Architecture. Here's a detailed explanation:
Definition:
Architecture Principles: These are the fundamental rules and guidelines that inform and support the way in which an organization sets about fulfilling its mission. They affect all phases of the architecture process.
Role in TOGAF:
Guidance and Governance: Architecture Principles provide the foundation for making architecture-related decisions. They guide the development, maintenance, and usage of all architecture artifacts.
Consistency and Alignment: They ensure that all architecture activities are consistent with the overall business strategy and objectives, providing alignment across different architecture domains.
TOGAF ADM Phases:
Preliminary Phase: This phase includes the establishment of architecture principles that will guide the entire architecture effort.
Phase A: Architecture Vision: During this phase, the architecture principles are used to create the vision and scope of the architecture project, ensuring it aligns with the organization's goals.
Examples of Architecture Principles:
Business Principles: These might include ensuring that business processes are customer-focused.
Data Principles: Principles ensuring data accuracy and availability.
Application Principles: Guidelines for application interoperability and usability.
Technology Principles: Standards for technology choices and infrastructure management.
In summary, architecture principles govern the architecture process, affecting its development, maintenance, and use, thereby ensuring alignment with business goals and consistency in architectural decisions.
Which ADM phase focuses on defining the problem to be solved, identifying the stakeholders, their concerns, and requirements?
Answer : A
Phase A of the TOGAF ADM (Architecture Development Method), also known as the Architecture Vision phase, focuses on defining the problem to be solved, identifying stakeholders, their concerns, and requirements. Here's a detailed explanation:
Phase A: Architecture Vision:
Objective: The primary objective of Phase A is to establish a high-level vision of the architecture project, including defining the scope and identifying key stakeholders and their concerns.
Problem Definition: This phase involves clearly defining the business problem or opportunity that the architecture project seeks to address. This sets the stage for all subsequent architecture work.
Stakeholder Identification:
Identification and Analysis: Stakeholders are identified and their concerns and requirements are gathered. This includes business leaders, IT leaders, end-users, and other relevant parties.
Understanding Needs: Understanding the needs and expectations of stakeholders is crucial for ensuring that the architecture aligns with business objectives and addresses key concerns.
Requirements Gathering:
High-Level Requirements: In Phase A, high-level requirements are identified and documented. These requirements guide the development of the architecture vision and provide a basis for more detailed requirements in later phases.
Requirements Management: A requirements management process is established to ensure that stakeholder needs are continuously captured, analyzed, and addressed throughout the architecture development process.
TOGAF Reference:
Deliverables: Key deliverables of Phase A include the Architecture Vision document, stakeholder map, and high-level requirements.
ADM Guidelines: TOGAF provides guidelines and techniques for conducting Phase A, including methods for stakeholder analysis, problem definition, and developing the architecture vision.
In summary, Phase A of the TOGAF ADM focuses on defining the problem to be solved, identifying stakeholders, understanding their concerns and requirements, and developing a high-level architecture vision that aligns with business objectives.