PMI-SP PMI Scheduling Professional Exam Practice Test
Mark is the project manager of the GHQ Project. He is happily reporting that his project has a schedule performance index of 2.12. Management, however, does not think this is good news. What is the most likely reason why management does not like an SPI of 2.12?
Answer : A
Cost and schedule performance indexes should be as close to 1 as possible. A larger value, such as 2.12, means that the schedule duration estimates were likely bloated or incorrect to begin with. Answer option B is incorrect. This is not the best choice for this question. Answer option C is incorrect. The number should not be close to 100; it should be close to 1. Answer option D is incorrect. While Mark may have crashed the schedule and driven up costs to achieve the SPI value, a more likely reason is that the time estimates were bloated.
You are the project manager of the NHQ Project. You have created the project network diagram as shown in the figure:
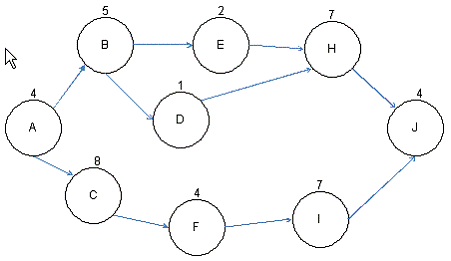
Based on the project network diagram, how much float is available for Activity H if Activity B is delayed by four days and Activity D is delayed by two days?
Answer : D
The path of ABDHJ will take 21 days to complete and cannot exceed 27 days or else the project will
be late. If Activity B takes four additional
days and Activity D takes two additional days, this adds (4+2= 6) six days to the path, bringing the
path's duration to exactly (21+6 = 27)
twenty seven days. There is no available float left for Activity E or H.
Float or total float (TF) is the total amount of time that a schedule activity may be delayed from its
early start date without delaying the
project finish date, or violating a schedule constraint. It is calculated by using the critical path
method technique and determining the
difference between the early finish dates and late finish dates.
Answer options A, C, and B are incorrect. There is no float available because the path's duration has
increased to 27 days.
You are the project manager for your project. Your project is scheduled to last for one year and you
are currently forty percent complete with
the project. Based on your current performance measurements you have an SPI of .95 and a cost
variance of -$24,000. You need to report
this information to the management, but you will also need a solution to present with the variance
information. Which one of the following can
you present to the management as a part of the control schedule tools and techniques for
variances?
Answer : B
The only tool and technique for controlling the schedule is a corrective action. You
should always report problems to management, the project
customers, or key stakeholders as defined in the Communications Management Plan, but you should
also always present a solution to the
problem.
A corrective action is a change implemented to address a weakness identified in a management
system. Normally corrective actions are
implemented in response to a customer complaint, abnormal levels of internal nonconformity,
nonconformities identified during an internal
audit or adverse or unstable trends in product and process monitoring such as would be identified
by SPC. It is method of identifying and
eliminating the causes of a problem, thus preventing their reappearance. Examples of a corrective
action are :
Improvements to maintenance schedules
Improvements to material handling or storage
Answer option C is incorrect. Trimming the project scope, which is a change request, is not a tool
and technique for control the scheduling. It
is, however, an output of the control schedule process and is sometimes a valid decision if the
project is slipping on schedule performance.
Answer option A is incorrect. Work performance measurements are not a tool and technique for
controlling the project schedule.
Answer option D is incorrect. The causes of the variance can help you determine the best action to
take, but it is not a tool and technique for
schedule control.
You are the project manager of the QAQ Project. The QAQ Project has a BAC of $2,786,121. You are
currently 20 percent complete with this project, though you should be 25 percent complete with the
project work. The project has consumed $595,000 of the project budget to date. Management has
asked you, based on the current project performance, what the project's estimate to complete will
be considering the current project schedule variance. What is the ETC for this project?
Answer : D
The estimate to complete wants to know how much more money the project will need
to complete its objectives.
The estimate to complete (ETC) is the expected cost needed to complete all the remaining work for a
scheduled activity, a group of activities,
or the project. ETC helps project managers predict what the final cost of the project will be upon
completion. The formula for the ETC is EAC-
AC. The EAC is BAC/CPI.
Answer option A is incorrect. This is the estimate at completion based on the current project
performance.
Answer option C is incorrect. This is the current schedule variance.
Answer option B is incorrect. 1.02 is the to-complete performance index based on the BAC.
All of the following statements about the critical path are false except for which one?
Answer : D
The only statement that is true is that the critical path shows the project's earliest date
for completion.
A critical path is the sequence of project activities, which add up to the longest overall duration. This
determines the shortest time possible to
complete the project. Any delay of an activity on the critical path directly impacts the planned
project completion date (i.e. there is no float on
the critical path). A project can have several, parallel, near critical paths. An additional parallel path
through the network with the total
durations shorter than the critical path is called a sub-critical or non-critical path.
These results allow managers to prioritize activities for the effective management of project
completion, and to shorten the planned critical
path of a project by pruning critical path activities, by 'fast tracking' (i.e., performing more activities
in parallel), and/or by 'crashing the critical
path' (i.e., shortening the durations of critical path activities by adding resources).
Answer option C is incorrect. There can be more than one critical path, as two paths in the project
network diagram can both take the same
amount of time and be longer than any other paths in the project.
Answer option A is incorrect. The critical path can be, and often is, crashed with extra resources in
an attempt to recover the project schedule.
Answer option B is incorrect. The critical path is the longest path to project completion.
You are the project manager for your organization. Management has offered you a bonus if you can complete the project work two months earlier than what your schedule predicts. You can use a schedule compression technique, but management does not want to increase costs in the project. What approach would you recommend to condense the project duration?
Answer : A
Of all the choices, only fast tracking is an option that would not increase project costs. Fast tracking
allows phases of the project to overlap,
but it does increase project risks.
Fast tracking is a technique for compressing project schedule. In fast tracking, phases are overlapped
that would normally be done in
sequence. It is shortening the project schedule without reducing the project scope.
Answer option B is incorrect. Crashing adds labor to the project and increases project costs.
Answer option C is incorrect. Effort-driven activity analysis examines activities whose duration may
be reduced by adding labor. This approach,
however, increases project costs, as it is a form of project crashing.
Answer option D is incorrect. Rewards and recognitions are good incentives for the project team, but
simply offering the reward does not
decrease the duration of the project.
Sam is the project manager for his organization. His project is not doing well on project schedule performance, and management wants him to predict how the project schedule and cost will end. Management has asked Sam to report and forecast his project's performance based on the Delphi Method, scenario building, technology forecasting, and to forecast by analogy. What forecasting method is management asking Sam to use?
Answer : A
Management is asking Sam to use the judgmental methods to predict how the project
will finish on time and cost.
The judgmental forecasting method incorporates intuitive judgments, opinions and subjective
probability estimates. Some examples of
judgmental forecasting are as follows:
Composite forecasts
Surveys
Delphi method
Scenario building
Technology forecasting
Forecast by analogy
Answer option B is incorrect. Time series methods of forecasting use earned value management,
moving average, extrapolation, linear
prediction, trend estimation, and growth curve.
Answer option D is incorrect. The earned value management method is actually a part of the time
series forecasting method.
Answer option C is incorrect. The causal/econometric methods use linear and non-linear regression,
autoregressive moving average, and
econometrics.