PECB ISO-IEC-27001-Lead-Auditor ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditor Exam Practice Test
You are performing an ISMS audit at a residential nursing home (ABC) that provides healthcare services. The next step in your audit plan is to verify the information security of ABC's healthcare mobile app development, support, and lifecycle process. During the audit, you learned the organization outsourced the mobile app development to a professional software development company with CMMI Level 5, ITSM (ISO/IEC 20000-1), BCMS (ISO 22301) and ISMS (ISO/IEC 27001) certified.
The IT Manager presented the software security management procedure and summarised the process as following:
The mobile app development shall adopt "security-by-design" and "security-by-default" principles, as a minimum. The following security
functions for personal data protection shall be available:
Access control.
Personal data encryption, i.e., Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm, key lengths: 256 bits; and
Personal data pseudonymization.
Vulnerability checked and no security backdoor
You sample the latest Mobile App Test report, details as follows:
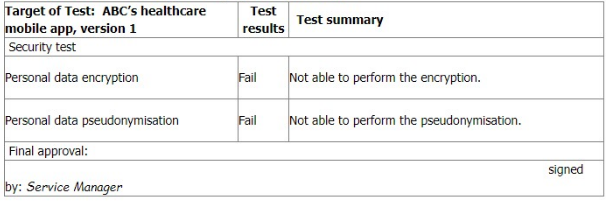
You ask the IT Manager why the organisation still uses the mobile app while personal data encryption and pseudonymization tests failed. Also, whether the Service Manager is authorised to approve the test.
The IT Manager explains the test results should be approved by him according to the software security management procedure.
The reason why the encryption and pseudonymisation functions failed is that these functions heavily slowed down the system and service performance. An extra 150% of resources are needed to cover this. The Service Manager agreed that access control is good enough and acceptable. That's why the Service Manager signed the approval.
You are preparing the audit findings. Select the correct option.
Scenario 8: EsBank provides banking and financial solutions to the Estonian banking sector since September 2010. The company has a network of 30 branches with over 100 ATMs across the country.
Operating in a highly regulated industry, EsBank must comply with many laws and regulations regarding the security and privacy of dat
a. They need to manage information security across their operations by implementing technical and nontechnical controls. EsBank decided to implement an ISMS based on ISO/IEC 27001 because it provided better security, more risk control, and compliance with key requirements of laws and regulations.
Nine months after the successful implementation of the ISMS, EsBank decided to pursue certification of their ISMS by an independent certification body against ISO/IEC 27001 .The certification audit included all of EsBank's systems, processes, and technologies.
The stage 1 and stage 2 audits were conducted jointly and several nonconformities were detected. The first nonconformity was related to EsBank's labeling of information. The company had an information classification scheme but there was no information labeling procedure. As a result, documents requiring the same level of protection would be labeled differently (sometimes as confidential, other times sensitive).
Considering that all the documents were also stored electronically, the nonconformity also impacted media handling. The audit team used sampling and concluded that 50 of 200 removable media stored sensitive information mistakenly classified as confidential. According to the information classification scheme, confidential information is allowed to be stored in removable media, whereas storing sensitive information is strictly prohibited. This marked the other nonconformity.
They drafted the nonconformity report and discussed the audit conclusions with EsBank's representatives, who agreed to submit an action plan for the detected nonconformities within two months.
EsBank accepted the audit team leader's proposed solution. They resolved the nonconformities by drafting a procedure for information labeling based on the classification scheme for both physical and electronic formats. The removable media procedure was also updated based on this procedure.
Two weeks after the audit completion, EsBank submitted a general action plan. There, they addressed the detected nonconformities and the corrective actions taken, but did not include any details on systems, controls, or operations impacted. The audit team evaluated the action plan and concluded that it would resolve the nonconformities. Yet, EsBank received an unfavorable recommendation for certification.
Based on the scenario above, answer the following question:
Which option justifies the unfavorable recommendation for certification? Refer to scenario 8.
Answer : A
Scenario 4: Branding is a marketing company that works with some of the most famous companies in the US. To reduce internal costs. Branding has outsourced the software development and IT helpdesk operations to Techvology for over two years. Techvology. equipped with the necessary expertise, manages Branding's software, network, and hardware needs. Branding has implemented an information security management system (ISMS) and is certified against ISO/IEC 27001, demonstrating its commitment to maintaining high standards of information security. It actively conducts audits on Techvology to ensure that the security of its outsourced operations complies with ISO/IEC 27001 certification requirements.
During the last audit. Branding's audit team defined the processes to be audited and the audit schedule. They adopted an evidence based approach, particularly in light of two information security incidents reported by Techvology in the past year The focus was on evaluating how these incidents were addressed and ensuring compliance with the terms of the outsourcing agreement
The audit began with a comprehensive review of Techvology's methods for monitoring the quality of outsourced operations, assessing whether the services provided met Branding's expectations and agreed-upon standards The auditors also verified whether Techvology complied with the contractual requirements established between the two entities This involved thoroughly examining the terms and conditions in the outsourcing agreement to guarantee that all aspects, including information security measures, are being adhered to.
Furthermore, the audit included a critical evaluation of the governance processes Techvology uses to manage its outsourced operations and other organizations. This step is crucial for Branding to verify that proper controls and oversight mechanisms are in place to mitigate potential risks associated with the outsourcing arrangement.
The auditors conducted interviews with various levels of Techvology's personnel and analyzed the incident resolution records. In addition, Techvology provided the records that served as evidence that they conducted awareness sessions for the staff regarding incident management. Based on the information gathered, they predicted that both information security incidents were caused by incompetent personnel. Therefore, auditors requested to see the personnel files of the employees involved in the incidents to review evidence of their competence, such as relevant experience, certificates, and records of attended trainings.
Branding's auditors performed a critical evaluation of the validity of the evidence obtained and remained alert for evidence that could contradict or question the reliability of the documented information received. During the audit at Techvology, the auditors upheld this approach by critically assessing the incident resolution records and conducting thorough interviews with employees at different levels and functions. They did not merely take the word of Techvology's representatives for facts; instead, they sought concrete evidence to support the representatives' claims about the incident management processes.
Based on the scenario above, answer the following question:
Based on Scenario 4, what type of audit did Branding conduct?
Answer : B
Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth
B . Correct Answer:
A second-party audit is conducted by an organization on its suppliers or outsourced service providers to ensure compliance with contractual and regulatory requirements.
Branding audited Techvology, an outsourced IT service provider, making this a second-party audit.
A . Incorrect:
A first-party audit is an internal audit, but Techvology is not an internal entity.
C . Incorrect:
A third-party audit is performed by an independent certification body, which is not the case here.
Relevant Standard Reference:
You are performing an ISMS audit at a residential nursing home called ABC that provides healthcare services. You find all nursing home residents wear an electronic wristband for monitoring their location, heartbeat, and blood pressure always. You learned that he electronic wristband automatically uploads all data to the artificial intelligence (AI) cloud server for healthcare monitoring and analysis by healthcare staff.
To verify the scope of ISMS, you interview the management system representative (MSR) who explains that the ISMS scope covers an outsourced data center.
Select four options for the clauses and/or controls of ISO/IEC 27001:2022 that are directly relevant to the verification of the scope of the ISMS.
Answer : B, E, F, H
You are an audit team leader who has just completed a third-party audit of a mobile telecommunication provider. You are preparing your audit report and are just about to complete a section headed 'confidentiality'.
An auditor in training on your team asks you if there are any circumstances under which the confidential report can be released to third parties.
Which four of the following responses are false?
Answer : A, F, G, H
The audit report is a confidential document that contains sensitive information about the auditee's ISMS and its performance. The audit team has a duty to protect the confidentiality of the audit report and only disclose it to authorized parties, such as the audit client, the certification body, and the accreditation body. Therefore, the following responses are false:
A: The audit team cannot decide to release the report to third parties without the consent of the audit client, as this would breach the confidentiality agreement and the audit code of conduct. The audit team should always inform the audit client before disclosing the report to any third party, and obtain their explicit, prior approval.
F: Not every auditor employed by the auditing organization can access the audit report, as this would violate the principle of need-to-know. Only auditors who are involved in the audit process, such as the audit team leader, the audit team members, the audit programme manager, and the certification decision maker, can access the audit report. Other auditors who are not related to the audit have no legitimate reason to access the report, and should be prevented from doing so by appropriate security measures.
G: The duty of confidentiality does not expire after a certain period of time, as this would compromise the trust and integrity of the audit process. The audit report remains confidential indefinitely, unless there is a legal or contractual obligation to disclose it, or the audit client agrees to release it. Third parties cannot access the audit report by making a subject access request, as this would infringe the privacy and data protection rights of the audit client and the auditee.
H: Subcontracted auditors are not considered to be third parties regarding confidentiality, as they are part of the audit team and have a contractual relationship with the auditing organization. Subcontracted auditors are typically bound by the same confidentiality agreement and audit code of conduct as the employed auditors, and have the same rights and responsibilities to access and protect the audit report.
ISO/IEC 27001:2022, clause 9.2, Internal audit
ISO/IEC 27006:2015, clause 7.2.3, Confidentiality
PECB Candidate Handbook ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, page 22, Audit Report
PECB Candidate Handbook ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, page 24, Audit Code of Conduct
You are performing an ISMS audit at a residential nursing home railed ABC that provides healthcare services. The next step in your audit plan is to verify the effectiveness of the continual improvement process. During the audit, you learned most of the residents' family members (90%) receive WeCare medical device promotional advertisements through email and SMS once a week via ABC's healthcare mobile app. All of them do not agree on the use of the collected personal data (or marketing or any other purposes than nursing and medical care on the signed service agreement with ABC. They have very strong reason to believe that ABC is leaking residents' and family members' personal information to a non-relevant third party and they have filed complaints.
The Service Manager says that all these complaints have been treated as nonconformities, and the corrective actions have been planned and implemented according to the Nonconformity and Corrective management procedure. The corrective action involved stopping working with WeCare the medical device manufacturer immediately and asking them to delete all personal data received as well as sending an apology email to all residents and their family members.
You are preparing the audit findings. Select one option of the correct finding.
Answer : A
In this case, ABC is a residential nursing home that provides healthcare services to its residents and collects their personal data and their family members' personal data. ABC has a signed service agreement with the residents' family members that states that the collected personal data will not be used for marketing or any other purposes than nursing and medical care. However, ABC has violated this contractual requirement by sharing the personal data with WeCare, a medical device manufacturer, who has used the data to send promotional advertisements to the residents' family members via email and SMS. This has caused dissatisfaction and complaints from the residents' family members, who have a strong reason to believe that ABC is leaking their personal information to a non-relevant third party.
Therefore, the audit finding is a nonconformity with clause 8.1.4 of ISO 27001:2022, as ABC has failed to control the externally provided processes, products or services that are relevant to the information security management system, and has breached the contractual requirements related to information security with its customers. The fact that ABC has taken corrective actions to stop working with WeCare and to apologise to the customers does not eliminate the nonconformity, but only mitigates its consequences. The nonconformity still needs to be recorded, evaluated, and reviewed for effectiveness and improvement.
You are performing an ISMS audit at a residential nursing home that provides healthcare services. The next step in your audit plan is to verify that the Statement of Applicability (SoA) contains the necessary controls. You review the latest SoA (version 5) document, sampling the access control to the source code (A.8.4), and want to know how the organisation secures ABC's healthcare mobile app source code received from an outsourced software developer.
The IT Security Manager explains the received source code will be checked into the SCM system to make sure of its integrity and security. Only authorised users will be able to check out the software to update it. Both check-in and check-out activities will be logged by the system automatically. The version control is managed by the system automatically.
You found a total of 10 user accounts on the SCM. All of them are from the IT department. You further check with the Human Resource manager and confirm that one of the users, Scott, resigned 9 months ago. The SCM System Administrator confirmed Scott's last check-out of the source code was found 1 month ago. He was using one of the authorised desktops from the local network in a secure area.
You check the user de-registration procedure which states "Managers have to make sure of deregistration of the user account and authorisation immediately from the relevant ICT system and/or equipment after resignation approval." There was no deregistration record for user Scott.
The IT Security Manager explains that Scott is a very good software engineer, an ex-colleague, and a friend. He still comes back to the office every month after he resigned to provide support on source code maintenance. That's why his account on SCM still exists. "We know Scott well and he passed all our background checks when he joined us. As such we didn't feel it necessary to agree any further information security requirements with him just because he is now an external provider".
You prepare the audit findings. Select the three correct options.
Answer : B, C, F
The correct options are:
There is a nonconformity (NC). The organisation's access control arrangements are not operating effectively as an individual who is no longer employed by the organisation is being permitted to access the nursing home's ICT systems. This does not conform with control A.5.15. (B): This option is correct because control A.5.15 requires the organization to implement secure log-on procedures and manage user access rights. The organization should ensure that only authorized users can access the ICT systems and that the access rights are revoked or modified when the user status changes. The fact that Scott, who resigned 9 months ago, still has an active account on the SCM and can check out the source code, indicates a failure of the access control arrangements and a nonconformity with the control A.5.15.
There is a nonconformity (NC). The IT Security manager did not make sure the user account for Scott was removed from the SCM and did not complete the user deregistration process after the resignation. This does not conform with clause 9.1 and control A.5.15. : This option is correct because clause 9.1 requires the organization to monitor, measure, analyze, and evaluate the performance and effectiveness of the ISMS. The organization should have processes and indicators to verify that the ISMS requirements and objectives are met and that the ISMS is continually improved. The organization should also ensure that the results of the monitoring and measurement are documented and communicated. The fact that the IT Security manager did not follow the user de-registration procedure and did not document or communicate the exception for Scott, indicates a failure of the monitoring and measurement processes and a nonconformity with clause 9.1 and control A.5.15.
There is a nonconformity (NC). The organisation has failed to identify the security risks associated with leaving Scott's account open when he was only re-engaged for a short period monthly. This does not conform with clause 8.2. (F): This option is correct because clause 8.2 requires the organization to establish and maintain an information security risk management process. The organization should identify the information security risks, analyze and evaluate the risks, and treat the risks according to the risk criteria and the risk treatment options. The organization should also monitor and review the risks and the risk treatment plan periodically and document the results. The fact that the organization did not identify the security risks associated with Scott's access to the SCM and the source code, such as unauthorized disclosure, modification, or deletion of the information, indicates a failure of the risk management process and a nonconformity with clause 8.2.