NetApp NS0-593 NetApp certified support engineer - ONTAP specialist Exam Practice Test
Your customer is running a NetApp AFF A800 system with NetApp ONTAP 9.8 software and states that their NS224 shelf is not showing with the correct shelf ID. You analyze the data and the shelf shows an identification of ''1.SHFHUXXXXXXXXXX."
What is the cause of the reported Issue?
A customer's storage administrator Informs you about the deactivated Automatic Switchover (AUSO) feature on their MetroCluster IP environment.
What Information would you tell your customer in this scenario?
Answer : B
Therefore, you would tell your customer that the AUSO feature is not available in MetroCluster IP installations by design, and that they need to use the ONTAP Mediator service instead for disaster recovery.Reference:
2: Differences among the ONTAP MetroCluster configurations, ONTAP MetroCluster Documentation Center
Your customer mentions that they have accidentally destroyed both root aggregates in their two-node cluster.
In this scenario, what are two actions that must be performed? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, C
If both root aggregates are destroyed in a two-node cluster, the cluster will be inoperable and the data will be inaccessible. To recover from this situation, you need to perform the following actions:
Install ONTAP from a USB device on one of the nodes. This will create a new root aggregate and a new cluster on that node.
Rejoin the second node to the re-created cluster. This will also create a new root aggregate on the second node and synchronize it with the first node.
Restore the cluster configuration and data from a backup, if available.Reference=
Storage System Recovery Troubleshooting
Recovering from a root aggregate failure
Refer to the exhibit.
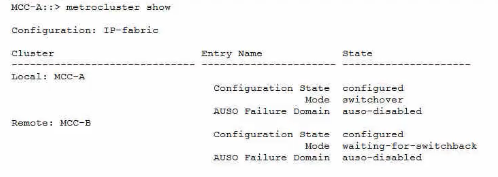
Referring to the exhibit, what do you need to do to return the MetroCluster to a normal state?
Answer : B
The other options are not correct, because:
Understanding MetroCluster data protection and disaster recovery - NetApp
Perform IP MetroCluster switchover and switchback - NetApp
Performing a switchback - NetApp
High-availability configuration - NetApp
You created a new NetApp ONTAP FlexGroup volume spanning six nodes and 12 aggregates with a total size of 4 TB. You added millions of files to the FlexGroup volume with a flat directory structure totaling 2 TB, and you receive an out of apace error message on your host.
What would cause this error?
You have a NetApp ONTAP cluster consisting of four NetApp FAS8200 controllers with two NetApp CN1610 cluster switches running ONIAP 9.8 software. You are receiving several alert messages stating that the cluster network has degraded. After troubleshooting, you determine that the errors are being generated from Node 2, interface e0b.
In this scenario, what should you do first to solve this problem?
Answer : A
A Twinax cable is a type of copper cable that is used to connect cluster ports to cluster switches1.
A cluster port is a network port that is configured for cluster communication and data access2.
A cluster network can be degraded due to various reasons, such as misconfiguration, malfunction, or excessive link errors on the cluster ports or the cluster switches.
Link errors are errors that occur on the physical layer of the network, such as CRC errors, length errors, alignment errors, or dropped packets.
Link errors can indicate a problem with the cable, the switch port, the network interface card (NIC), or the cable connector.
In this scenario, the alert messages state that the cluster network has degraded and the errors are being generated from Node 2, interface e0b.
The first step to solve this problem is to replace the Twinax cable between Node 2, interface e0b and the NetApp CN1610 switch, as this could be the source of the link errors.
Replacing the cable could resolve the issue and restore the cluster network to a healthy state.
If replacing the cable does not solve the problem, then other steps may be required, such as checking the switch port, the NIC, or the cable connector, or replacing the switch or the motherboard.Reference:
1: Cluster network cabling, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
2: Cluster ports, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
3: Cluster switches, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
4: Cluster network, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
[5]: How to troubleshoot CLUSTER NETWORK DEGRADED error messages, NetApp Knowledge Base
[6]: Cluster network degraded due to high CRC errors on cluster ports, NetApp Knowledge Base
A customer enabled NFSv4.0 on an SVM and changed the client mount from NFSv3 to NFSv4. Afterwards, the customer found that the directory owner was changed from root to nobody.
In this scenario, which statement is true?
Answer : D