Microsoft Designing and Implementing Microsoft Azure Networking Solutions AZ-700 Exam Questions
You need to configure the default route in Vnet2 and Vnet3. The solution must meet the virtual networking requirements.
What should you use to configure the default route?
Answer : C
VNet 1 will get the default from BGP and propagate it to VNET 2 and 3
You plan to publish a website that will use an FQDN of www.contoso.com. The website will be hosted by using the Azure App Service apps shown in the following table.
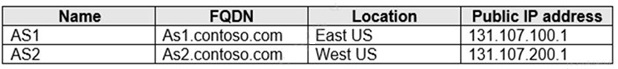
You plan to use Azure Traffic Manager to manage the routing of traffic for www.contoso.com between AS1 and AS2.
You need to ensure that Traffic Manager routes traffic for www.contoso.com.
Which DNS record should you create?
Answer : C
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/traffic-manager/quickstart-create-traffic-manager-profile
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/configure-domain-traffic-manager
Your company has an office in New York.
The company has an Azure subscription that contains the virtual networks shown in the following table.
Name
Location
Vnet1
East LS
Vnet2
North Europe
Vnet3
West US
Vnet4
West Europe
You need to connect the virtual networks to the office by using ExpressRoute. The solution must meet the following requirements:
* The connection must have up to 1 Gbps of bandwidth.
* The office must have access to all the virtual networks.
* Costs must be minimized.
How many ExpressRoute circuits should be provisioned, and which ExpressRoute 5KU should you enable?
Answer : B
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Virtual WAN named VWAN1. VWAN1 contains a hub named Hub1.
Hub1 has a security status of Unsecured.
You need to ensure that the security status of Hub1 is marked as Secured.
Solution: You implement Azure Web Application Firewall (WAF).
Does this meet the requirement?
Answer : B
You have two Azure subscriptions named Sub1 and Sub2. Sub1 contains a virtual machine named VM1.
You plan to make VM1 available to the resources in Sub2 by using Azure Private Link.
You need to ensure that the private link service can be configured to provide access to VM1.
What should you configure in Sub1 first?
Answer : C
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure subscription that contains the following resources:
* A virtual network named Vnet1
* A subnet named Subnet1 in Vnet1
* A virtual machine named VM1 that connects to Subnet1
* Three storage accounts named storage1, storage2. and storage3
You need to ensure that VM1 can access storage1. VM1 must be prevented from accessing any other storage accounts.
Solution: You create a network security group (NSG). You configure a service tag for MicrosoftStorage and link the tag to Subnet1.
Does this meet the goal?
Answer : B
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have on Azure subscription that contains on Azure Virtual WAN named VWAN1.VWAN1 contains a hub named Hub1.
Hub! has a security status of Unsecured.
You need to ensure that the security status of Hub1 is marked as Secured.
Solution: You implement Azure Firewall.
Does this meet the requirement?
Answer : B