LPIC-3: Mixed Environments - Exam 300 - version 3.0 300-300 Exam Practice Test
Which of the following lines is missing in the given [printers] share definition?
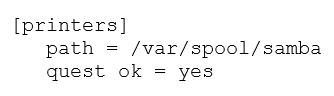
Answer : B
In the context of a Samba configuration for printer shares, the [printers] section usually requires the printable = yes directive to indicate that the share is meant for printing. Without this directive, Samba would not treat the share as a printer share, even if other settings like path are configured properly.
The given snippet is:
The line printable = yes is missing and is essential for defining a printer share.
Samba Official Documentation - Printer Sharing
Which of the following Group Policy Objects exist by default in an Active Directory domain? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, B
Default Group Policy Objects in AD:
A . Default Domain Policy: This is a built-in GPO that is applied to all users and computers in the domain. It contains security settings, password policies, and other domain-wide configurations.
B . Default Domain Controllers Policy: This GPO is specifically applied to the Domain Controllers organizational unit (OU). It contains settings relevant to domain controllers, such as security settings and audit policies.
Active Directory Group Policy documentation
Best practices for managing Group Policy in Active Directory
Which of the following statements about automount in a FreeIPA domain are true? (Choose two.)
Answer : C, D
Automounting in a FreeIPA domain involves several key aspects:
Base Configuration File (/etc/auto.master): The auto.master file is the main configuration file for the automounter. It contains the master map which defines mount points and their corresponding maps. This file is crucial for setting up automount points.
Example entry in /etc/auto.master:
plaintext
Copy code
/home /etc/auto.home
SSSD Requirement: In a FreeIPA domain, automount requires the System Security Services Daemon (SSSD) to be installed and configured on each client. SSSD is used to retrieve automount maps from the FreeIPA server, enabling the automount feature to function correctly.
Example configuration in /etc/sssd/sssd.conf:
[sssd] services = nss, pam, autofs config_file_version = 2 domains = example.com [domain/example.com] autofs_provider = ipa ipa_server = _srv_
Automount Configuration
FreeIPA SSSD Integration
Which of the following commands terminates all running instances of the Samba daemon handling for SMB shares?
Answer : D
Samba is a suite of programs that allows SMB/CIFS clients to interact with file and print services on a Linux/UNIX server.
smbd is the Samba daemon responsible for handling SMB/CIFS requests.
The smbcontrol utility is used to send messages to running Samba daemons.
The correct way to terminate all running instances of the Samba daemon handling SMB shares is to send a shutdown message to smbd using the command smbcontrol smbd shutdown.
This command ensures that only the smbd processes, which are responsible for handling SMB shares, are terminated without affecting other Samba components like nmbd (NetBIOS name server daemon).
Samba documentation: https://www.samba.org/samba/docs/current/man-html/smbcontrol.1.html
FILL in BLANK
What option in sms.conf defines where the data of a file share is stored? (Specify ONLY the option name without any values.)
Answer : A
path Option: This parameter in smb.conf specifies the directory on the server where the shared data is stored.
Usage: Within a share definition, the path option points to the actual location on the filesystem that Samba will share.
Example Configuration:
[example_share] path = /srv/samba/share
Importance: Defining the correct path is crucial for ensuring that the share points to the intended directory with the appropriate data and permissions.
Samba smb.conf man page
What is a correct statement about FreeIPA ID views?
Answer : C
In FreeIPA, ID views allow administrators to override default POSIX attributes for users and groups. This feature is useful when integrating with other identity management systems, enabling specific attribute values to be used on a per-host basis. This way, different POSIX attributes can be set for the same user or group in different contexts.
FreeIPA: ID Views
FreeIPA Documentation
When using rsync to synchronize the SYSVOL share's contents between multiple Samba servers, which of the following precautions should be taken? (Choose three.)
Answer : A, C, E
When using rsync to synchronize the SYSVOL share's contents between multiple Samba servers, it's essential to ensure data consistency and avoid conflicts. The following precautions should be taken:
A . Synchronize from the domain controller which is the PDC emulator to the other domain controllers.
The PDC emulator is typically the authoritative source for certain domain-wide operations, making it the best source for SYSVOL synchronization.
C . Make the SYSVOL share read only on all domain controllers but the one used as synchronization source.
This prevents changes on other domain controllers that could cause inconsistencies.
E . Make sure to make all changes to GPOs on the domain controller which is the replication source.
Ensuring that all Group Policy Objects (GPOs) changes are made on the source controller prevents conflicts and ensures that all controllers have the latest configuration.
Samba Documentation - SYSVOL Replication