Juniper Data Center Professional JN0-683 Exam Questions
You want to provide a OCI that keeps each data center routing domain isolated, while also supporting translation of VNIs. Which DCI scheme allows these features?
Answer : C
Understanding DCI (Data Center Interconnect) Schemes:
DCI schemes are used to connect multiple data centers, enabling seamless communication and resource sharing between them. The choice of DCI depends on the specific requirements, such as isolation, VNI translation, or routing domain separation.
VXLAN Stitching:
VXLAN stitching involves connecting multiple VXLAN segments, allowing VNIs (VXLAN Network Identifiers) from different segments to communicate with each other while maintaining separate routing domains.
This approach is particularly effective for keeping routing domains isolated while supporting VNI translation, making it ideal for scenarios where you need to connect different data centers or networks without merging their control planes.
Other Options:
A . MPLS DCI label exchange: This option typically focuses on MPLS-based interconnections and does not inherently support VNI translation or isolation in the context of VXLAN.
B . Over the top (OTT) with VNI translation enabled: This could support VNI translation but does not inherently ensure routing domain isolation.
D . Over the top (OTT) with proxy gateways: This typically involves using external gateways for traffic routing and may not directly support VNI translation or isolation in the same way as VXLAN stitching.
Data Center Reference:
VXLAN stitching is a powerful method in multi-data center environments, allowing for flexibility in connecting various VXLAN segments while preserving network isolation and supporting complex interconnect requirements.
You are asked to configure telemetry on the OFX Series devices in your data center fabric. You want to use sensors that have a vendor-neutral data model Which type of sensor should you use in this scenario?
Answer : A
Telemetry in Data Centers:
Telemetry allows for real-time monitoring of network devices by collecting and exporting data such as interface statistics, routing table updates, and other key metrics.
Option A: JTI (Junos Telemetry Interface) OpenConfig sensors use a vendor-neutral data model, which is important for ensuring compatibility across different network devices and systems. OpenConfig is an industry-standard model, which facilitates integration with various telemetry collection systems.
Conclusion:
Option A: Correct---OpenConfig sensors provide a vendor-neutral solution for telemetry, ensuring broad compatibility and flexibility in data center environments.
Exhibit.
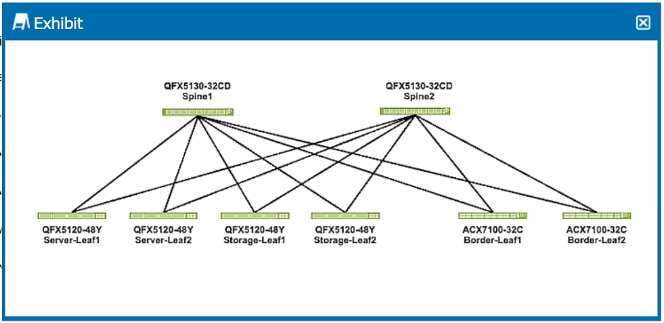
You are deploying a VXLAN overlay with EVPN as the control plane in an ERB architecture.
Referring to the exhibit, which three statements are correct about where the VXLAN gateways will be placed? (Choose three.)
Answer : B, C, E
Understanding ERB Architecture:
ERB (Edge Routed Bridging) architecture is a network design where the routing occurs at the edge (leaf devices) rather than in the spine devices. In a VXLAN overlay network with EVPN as the control plane, leaf devices typically act as both Layer 2 (L2) and Layer 3 (L3) VXLAN gateways.
Placement of VXLAN Gateways:
Option B: All leaf devices will have L2 VXLAN gateways to handle the bridging of VLAN traffic into VXLAN tunnels.
Option C: All leaf devices will also have L3 VXLAN gateways to route traffic between different VXLAN segments (VNIs) and external networks.
Option E: Spine devices in an ERB architecture generally do not function as VXLAN gateways. They primarily focus on forwarding traffic between leaf nodes and do not handle VXLAN encapsulation/decapsulation.
Conclusion:
Option B: Correct---All leaf devices will have L2 VXLAN gateways.
Option C: Correct---All leaf devices will have L3 VXLAN gateways.
Option E: Correct---Spine devices will not act as VXLAN gateways
Exhibit.
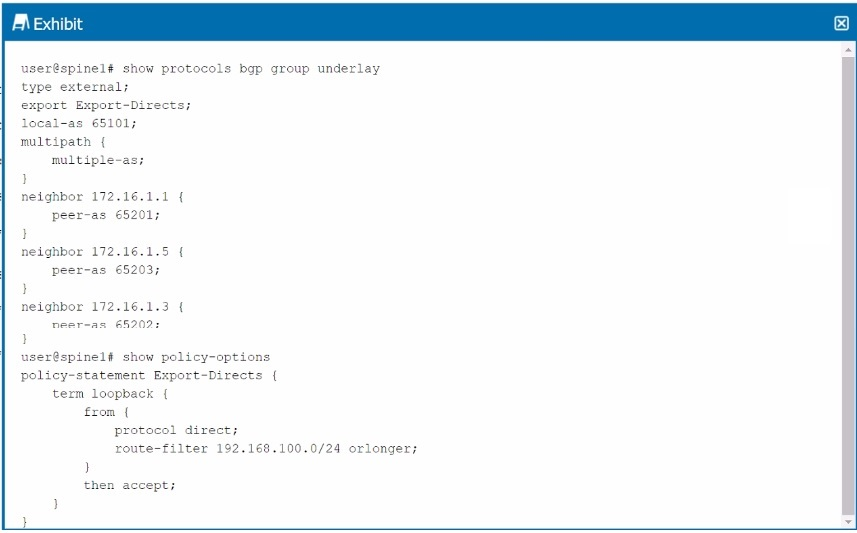
Referring to the exhibit, the spinel device has an underlay BGP group that is configured to peer with its neighbors' directly connected interfaces. Which two statements are true in this scenario? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, D
Understanding BGP Configuration in the Exhibit:
The exhibit shows a BGP configuration on spine1 with a group named underlay, configured to peer with directly connected interfaces of other devices in the network.
Multipath multiple-as: This statement allows the router to install multiple paths in the routing table for routes learned from different ASes, facilitating load balancing.
Key Statements:
A . The multihop statement is not required to establish the underlay BGP sessions: In this case, the BGP peers are directly connected (as indicated by their neighbor IP addresses), so the multihop statement is unnecessary. Multihop is typically used when BGP peers are not directly connected and packets need to traverse multiple hops.
D . Load balancing for the underlay is configured correctly: The multipath { multiple-as; } statement in the configuration enables load balancing across multiple paths from different autonomous systems, which is appropriate for underlay networks in data center fabrics.
Incorrect Statements:
C . The multihop statement is required to establish the underlay BGP sessions: This is incorrect because the peers are directly connected, making the multihop statement unnecessary.
B . Load balancing for the underlay is not configured correctly: This is incorrect because the configuration includes the necessary multipath settings for load balancing.
Data Center Reference:
BGP configurations in EVPN-VXLAN underlay networks are crucial for ensuring redundancy, load balancing, and efficient route propagation across the data center fabric.
What are three actions available tor MAC move limiting? (Choose three.)
Answer : A, D, E
MAC Move Limiting:
MAC move limiting is a security feature used in network switches to detect and mitigate rapid changes in MAC address locations, which could indicate a network issue or an attack such as MAC flapping or spoofing.
When a MAC address is learned on a different interface than it was previously learned, the switch can take various actions to prevent potential issues.
Available Actions:
A . drop: This action drops packets from the MAC address if it violates the move limit, effectively blocking communication from the offending MAC address.
D . log: This action logs the MAC move event without disrupting traffic, allowing network administrators to monitor and investigate the event.
E . shutdown: This action shuts down the interface on which the MAC address violation occurred, effectively stopping all traffic on that interface to prevent further issues.
Other Actions (Not Correct):
B . filter: Filtering is not typically associated with MAC move limiting; it generally refers to applying ACLs or other mechanisms to filter traffic.
C . enable: This is not an action related to MAC move limiting, as it does not represent a specific reaction to a MAC move event.
Data Center Reference:
MAC move limiting is crucial for maintaining network stability and security, particularly in environments with dynamic or large-scale Layer 2 networks where MAC addresses might frequently change locations.
You are designing an IP fabric tor a large data center, and you are concerned about growth and scalability. Which two actions would you take to address these concerns? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, D
Clos IP Fabric Design:
A Clos fabric is a network topology designed for scalable, high-performance data centers. It is typically arranged in multiple stages, providing redundancy, high bandwidth, and low latency.
Three-Stage Clos Fabric:
Option B: A three-stage Clos fabric, consisting of leaf, spine, and super spine layers, is widely used in data centers. This design scales well and allows for easy expansion by adding more leaf and spine devices as needed.
Super Spines for Scalability:
Option D: Using high-capacity devices like the QFX5700 Series as super spines can handle the increased traffic demands in large data centers and support future growth. These devices provide the necessary bandwidth and scalability for large-scale deployments.
Conclusion:
Option B: Correct---A three-stage Clos fabric is a proven design that addresses growth and scalability concerns in large data centers.
Option D: Correct---QFX5700 Series devices are suitable for use as super spines in large-scale environments due to their high performance.
Which parameter is used to associate a received route with a local VPN route table?
Answer : A
Understanding VPN Route Table Association:
In MPLS/VPN and EVPN networks, the route-target community is a BGP extended community attribute used to control the import and export of VPN routes. It associates received routes with the appropriate VPN route tables on the PE (Provider Edge) routers.
Function of Route-Target Community:
The route-target community tag ensures that routes are imported into the correct VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding) instance, allowing them to be correctly routed within the VPN.
Conclusion:
Option A: Correct---The route-target community is used to associate received routes with a local VPN route table.