Juniper JN0-636 Juniper Security, Professional JNCIP-SEC Exam Practice Test
you must find an infected host and where the aack came from using the Juniper ATP Cloud. Which two monitor workspaces will return the requested information? (Choose Two)
Answer : A, C
To find an infected host and where the attack came from using the Juniper ATP Cloud, you need to use the Hosts and Threat Sources monitor workspaces. The other options are incorrect because:
Therefore, the correct answer is A and C. You need to use the Hosts and Threat Sources monitor workspaces to find an infected host and where the attack came from using the Juniper ATP Cloud. To do so, you need to perform the following steps:
For Threat Sources, you need to access the Threat Sources monitor workspace in the Juniper ATP Cloud WebUI by selecting Monitor > Threat Sources. You can see the list of threat sources that have been detected by the Juniper ATP Cloud and their risk scores, threat categories, and geolocations. You can filter the threat sources by various criteria, such as IP address, domain, or threat category. You can also drill down into each threat source to see the details of the files, applications, and incidents associated with the threat source. You can identify the attack source by looking for the threat source with the highest risk score, threat category, or geolocation that matches the infected host.
[Threat Sources]
Which two types of source NAT translations are supported in this scenario? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, C
The two types of source NAT translations that are supported in this scenario are translation of IPv4 hosts to IPv6 hosts with or without port address translation, and translation of one IPv6 subnet to another IPv6 subnet without port address translation. These are the types of source NAT translations that are supported by the Junos OS for IPv6 NAT. Translation of IPv4 hosts to IPv6 hosts allows IPv4-only hosts to communicate with IPv6-only hosts by changing the source IPv4 address to a corresponding IPv6 address. Port address translation can be optionally enabled to conserve IPv6 addresses by using different port numbers for different sessions. Translation of one IPv6 subnet to another IPv6 subnet allows IPv6 hosts to use a different IPv6 address range for outbound traffic, such as for security or policy reasons. Port address translation is not supported for this type of translation, as IPv6 addresses are abundant and do not need to be conserved.Reference: Juniper Security, Professional (JNCIP-SEC) Reference Materials source and documents: https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/junos/topics/concept/security-nat-ipv6-overview.html
You are required to deploy a security policy on an SRX Series device that blocks all known Tor network IP addresses. Which two steps will fulfill this requirement? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, C
The two steps that will fulfill the requirement of deploying a security policy on an SRX Series device that blocks all known Tor network IP addresses are enrolling the devices with Juniper ATP Cloud and enabling a third-party Tor feed. Juniper ATP Cloud is a cloud-based service that provides advanced threat detection and mitigation capabilities for SRX Series devices. By enrolling the devices with Juniper ATP Cloud, the devices can leverage the cloud intelligence and analytics to identify and block malicious traffic, including Tor traffic. A third-party Tor feed is a source of information that provides a list of IP addresses that are associated with the Tor network. By enabling a third-party Tor feed on the SRX Series device, the device can use the feed to create a dynamic address object that contains all the known Tor IP addresses. The device can then apply a security policy that denies traffic from or to the dynamic address object, effectively blocking the Tor network IP addresses.Reference: Juniper Security, Professional (JNCIP-SEC) Reference Materials source and documents: https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/junos/topics/concept/security-atp-cloud-overview.html https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/junos/topics/task/configuration/security-intelligence-third-party-feed-configuring.html
Refer to the Exhibit:

which two statements about the configuration shown in the exhibit are correct ?
Answer : A, D
The two statements about the configuration shown in the exhibit are correct are:
The other statements are incorrect because:
C) The local IKE gateway IP address is not 203.0.113.100, but 192.0.2.100, as explained above.
Exhibit
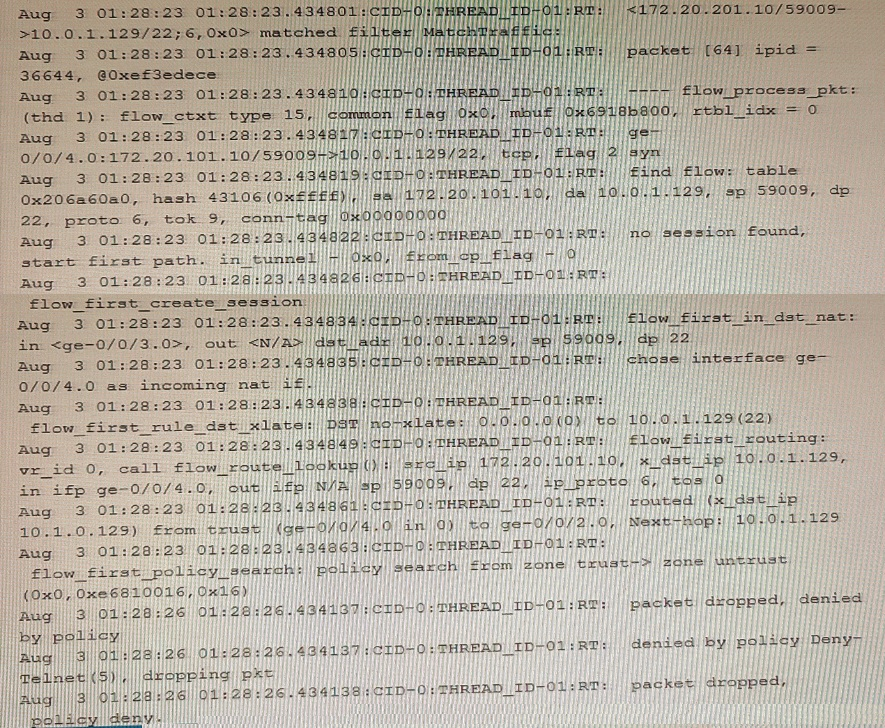
Which two statements are correct about the output shown in the exhibit. (Choose two.)
Answer : A, B
The source address is translated because the traceoptions output shows that the source IP address 192.168.5.2 is translated to 192.168.100.1 and the source port 0 is translated to 14777. The traceoptions output also shows the flag flow_first_src_xlate, which indicates that this is the first time that source NAT is applied to this session.
The packet is an SSH packet because the traceoptions output shows that the application protocol is tcp/22, which is the default port for SSH. The traceoptions output also shows the flag flow_tcp_syn, which indicates that this is the first packet of a TCP connection.
traceoptions (Security NAT) | Junos OS | Juniper Networks
[SRX] How to interpret Flow TraceOptions output for NAT troubleshooting
Your Source NAT implementation uses an address pool that contains multiple IPv4 addresses Your users report that when they establish more than one session with an external application, they are prompted to authenticate multiple times External hosts must not be able to establish sessions with internal network hosts
What will solve this problem?
Answer : D
The solution to this problem is to enable address persistence. This will ensure that the same external IP address is used for multiple sessions between an internal host and an external host. This will result in only one authentication being required, as the same external IP address will be used for all sessions.
Exhibit
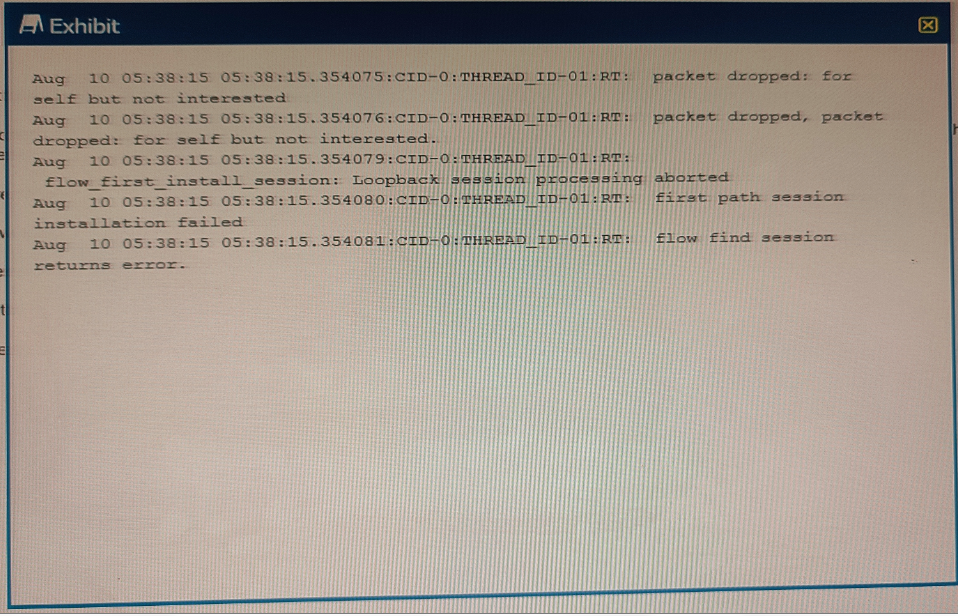
You are asked to establish an IBGP peering between the SRX Series device and the router, but the session is not being established. In the security flow trace on the SRX device, packet drops are observed as shown in the exhibit.
What is the correct action to solve the problem on the SRX device?
Answer : C
set security zones security-zone <zone-name> interfaces <interface-name> host-inbound-traffic system-services bgp