Juniper JN0-351 Enterprise Routing and Switching, Specialist Exam Practice Test
Which statement is correct about the storm control feature?
Answer : A
Option C is incorrect. There's no information available that suggests the storm control feature is not supported on aggregate Ethernet interfaces.
Exhibit

You are receiving the BGP route shown in the exhibit from four different upstream ISPs.
Referring to the exhibit, which ISP will be selected as the active path?
Answer : C
Which two statements correctly describe RSTP port roles? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, D
Therefore, options A and D are correct.
Exhibit.
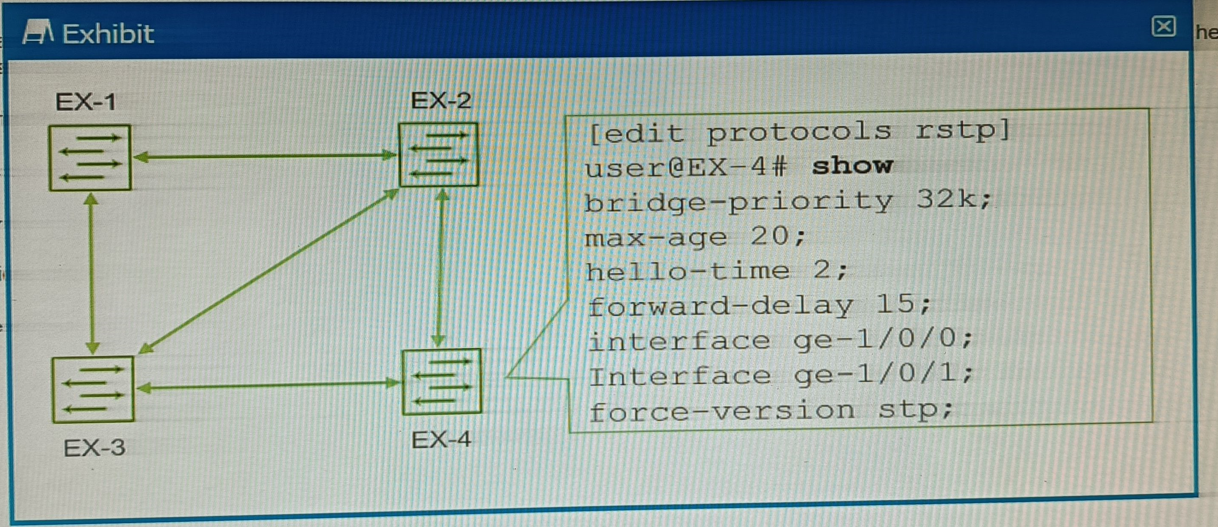
You have configured the four EX Series switches with RSTP, as shown in the exhibit. You discover that whenever a link between switches goes up or down, the switches take longer than expected for RSTP to converge, using the default settings.
In this scenario, which action would solve the delay in RSTP convergence?
Answer : B
You have two OSPF routers forming an adjacency. R1 has a priority of 32 and a router ID of 192.168.1.2. R2 has a priority of 64 and a router ID of 192.168.1.1. The routers were started at the same time and all other OSPF settings are the default settings.
Which statement is correct in this scenario?
Answer : D
You are asked to create a new firewall filter to evaluate Layer 3 traffic that is being sent between VLANs. In this scenario, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
Answer : C, D
Therefore, option C is correct, because you should create a family inet firewall filter with the appropriate match criteria and actions. Option D is correct, because you should apply the firewall filter to the appropriate IRB interface.
Which two statements are correct about tunnels? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, D
A tunnel is a connection between two computer networks, in which data is sent from one network to another through an encrypted link. Tunnels are commonly used to secure data communications between two networks or to connect two networks that use different protocols.
Option A is incorrect, because BFD can be used to monitor tunnels. BFD is a protocol that can be used to quickly detect failures in the forwarding path between two adjacent routers or switches. BFD can be integrated with various routing protocols and link aggregation protocols to provide faster convergence and fault recovery. BFD can also be used to monitor the connectivity of tunnels, such as GRE, IPsec, or MPLS.
Option C is incorrect, because IP-IP tunnels are stateless. IP-IP tunnels are a type of tunnels that use IP as both the encapsulating and encapsulated protocol. IP-IP tunnels are simple and easy to configure, but they do not provide any security or authentication features. IP-IP tunnels are stateless, which means that they do not keep track of the state or status of the tunnel connection. Stateless tunnels do not require any signaling or negotiation between the endpoints, but they also do not provide any error detection or recovery mechanisms.