Juniper Junos, Associate JN0-105 Exam Practice Test
You have just increased the MTU size of interface ge-0/0/0 and committed the configuration.
Which command would help you identify the applied MTU change?
Answer : D
After increasing the MTU size of an interface and committing the configuration, the command to verify the applied MTU change is D, 'show interfaces ge-0/0/0.' This command displays detailed information about the interface, including the current MTU size, making it the best choice for verifying the applied changes.
Which layer of the OSI model contains the IP address information?
Answer : B
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework used to understand network interactions in seven distinct layers. IP (Internet Protocol) addresses are part of Layer 3, known as the Network Layer. This layer is responsible for packet forwarding, including routing through intermediate routers, and it handles the logical addressing scheme of the network to ensure that packets can be routed across multiple networks and reach their destination. IP addresses provide unique identifiers for network interfaces, allowing for communication between devices on a network or across different networks.
Which protocol is responsible for learning an IPv4 neighbor's MAC address?
Answer : A
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is responsible for mapping an IPv4 address to a machine's MAC address. ARP operates at Layer 2 of the OSI model and is used to find the MAC address of a host given its IPv4 address. When a device wants to communicate with another device on the same local network, it uses ARP to discover the recipient's MAC address.
Juniper official documentation: ARP.
Networking standards: RFC 826.
You are asked to view the real-time usage statistics for the busiest interfaces on a device running Junos OS.
Which command will achieve this task?
Answer : B
To view real-time usage statistics for the busiest interfaces on a device running Junos OS, the correct command is B, 'monitor interface traffic.' This command provides a dynamic, real-time view of the traffic flowing through the interfaces, allowing administrators to quickly identify and monitor the busiest interfaces on the device.
You issue the monitor traffic interface ge-0/0/0 command.
What will this command accomplish?
Answer : D
The command 'monitor traffic interface ge-0/0/0' (D) initiates a packet capture on the specified interface, allowing you to view the actual packets being transmitted and received. This is useful for troubleshooting and analyzing the traffic passing through the interface in real time.
What are two attributes of the UDP protocol? (Choose two.)
Answer : C, D
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is known for being connectionless (D) and providing best-effort delivery without the reliability mechanisms present in TCP (C). This means that UDP does not establish a connection before sending data and does not guarantee delivery, order, or error checking, making it faster but less reliable than TCP.
Click the Exhibit button.
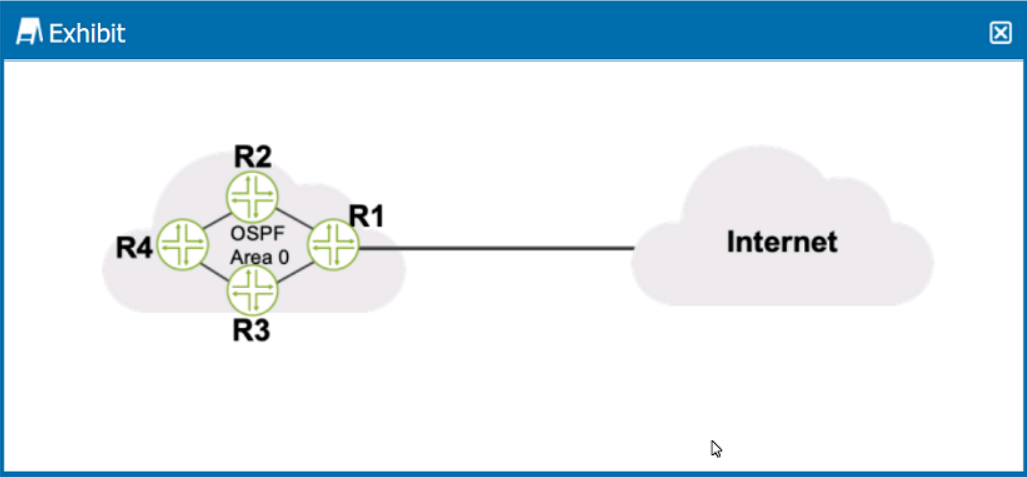
Referring to the exhibit, what should be configured on R1 to advertise a default static route into OSPF?
Answer : B
To advertise a default static route into OSPF on router R1, a routing policy should be configured. This policy would typically include a statement to match the default route (0.0.0.0/0) and then apply an action to set the route as an OSPF external type, which would then be redistributed into the OSPF domain. The routing policy is a set of conditions and actions that determine how routes are imported into or exported from the routing table and how routes are shared between routing instances or routing protocols. After defining the policy, it must be applied to OSPF under the export section of the OSPF configuration on R1. This process will allow R1 to announce the default route to other OSPF routers in the network, which then can use it as a gateway of last resort to reach the Internet or other networks not explicitly known to the OSPF domain.