HPE7-A07 Aruba Certified Campus Access Mobility Expert Written Exam Practice Test
Which data transmission method provides the most efficient use of airtime for VoIP traffic?
Answer : C
MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Output) provides the most efficient use of airtime for VoIP traffic among the options listed. MU-MIMO allows multiple users to receive multiple data streams simultaneously, improving the overall efficiency of the network, especially in dense environments where VoIP applications need consistent and reliable connectivity.
You deployed UBT to securely tunnel traffic from user desktop PCs connected behind VOIP phones Ail other non-UBT dents are connected to a different network. After the deployment users reported interruptions lo their phone service
Answer : A
If users report interruptions to their phone service after the deployment of User-Based Tunneling (UBT), it can be due to the VLAN designated for UBT clients not being configured on the switch uplink. As a result, traffic from VoIP phones, which may be trying to use the same VLAN, could be dropped, leading to service interruptions. Ensuring that the VLAN is properly configured on the switch uplink is crucial for the seamless operation of UBT clients and VoIP services.
Exhibit.
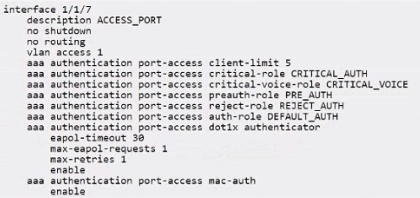
Which user role will be assigned when a voice client tries to connect for the first time, but the RADIUS server is unavailable?
Answer : C
In the provided configuration for interface 1/1/7, there are roles specified for different scenarios concerning authentication. When a voice client attempts to connect and the RADIUS server is unreachable, the role that is assigned is the one specified as the 'critical-voice-role'. In this case, the 'CRITICAL_VOICE' role is configured to be assigned under such circumstances, ensuring that voice clients receive appropriate network access permissions even when the RADIUS server is not available to authenticate them.
The ACME company has an AOS-CX 6200 switch stack with an uplink oversubscription ratio of 9.6:1. They are considering adding two more nodes to the stack without adding any additional uplinks due to cabling constraints One of their architects has expressed concerns that their critical UDP traffic from both wired and bridged AP clients will encounter packet drops. They have already applied the following configuration:

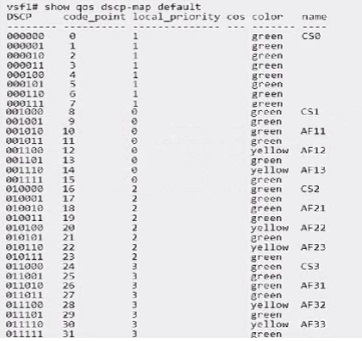
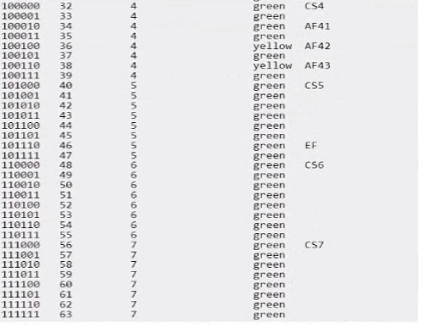
Which strategy will complement this solution to achieve their objective?
Answer : D
Given that the ACME company's concern is about UDP traffic potentially encountering packet drops due to uplink oversubscription, they need a strategy that prioritizes critical UDP traffic to minimize loss.
Option D, edge mark critical UDP traffic with AF42, is the correct answer. Assured Forwarding (AF) classes provide a way to assign different levels of delivery assurance for IP packets. AF42 is typically used for traffic that requires low latency and low loss, such as voice and video, which often use UDP. Marking critical UDP traffic with AF42 will help ensure that this traffic is treated with higher priority over the network.
Option A (edge mark lower priority TCP traffic with AF12) and Option C (edge mark lower priority TCP traffic with AF11) suggest marking lower priority TCP traffic, which does not directly address the concern for critical UDP traffic.
Option B (edge mark critical UDP Traffic with CS5) suggests using Class Selector 5 for critical UDP traffic, which is also a valid approach but does not match the existing configuration that is focused on Assured Forwarding (AF) classes.
An ACME company employee complained about a recent poor-quality VoIP call while moving around their office environment HPE Aruba Networking Central reported a fair UCC score for this call while your VoIP engineer reported that their systems reported a MOS of 2, 3. The VoIP devices are operating over the 5GHz frequency band.
What are the possible contributing factors? (Select two.)
Answer : A, E
VoIP quality can be negatively impacted by insufficient cell overlap in AP deployment plans, which can cause poor handoffs between APs as a user moves around. This results in a degraded VoIP experience. Additionally, roaming into an area with continuous Zigbee operation can cause interference with the 5GHz frequency band, further contributing to poor VoIP call quality. The Zigbee communication protocol operates on the same frequency band as Wi-Fi and can introduce noise and interference, which leads to a reduced MOS score, as reported by the VoIP engineer.
You configured" a bridged mode SSID with WPA3-Enterprise and EAP-TLS security. When you connect an Active Directory joined client that has valid client certificates. ClearPass shows the following error.
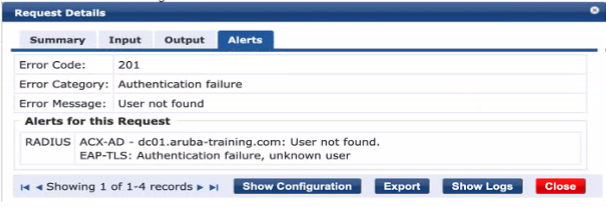
What is needed to resolve this issue?
Answer : C
The error message 'User not found' indicates that the authentication source, in this case, Active Directory (AD), is not able to locate the user account based on the current search parameters. This often occurs when the User Principal Name (UPN) that the client is using to authenticate is not included in the search parameters of the AD authentication source within ClearPass. By modifying the AD authentication source to include the UPN in the search, ClearPass will be able to correctly locate the user account and proceed with the authentication using the valid client certificates.
Exhibit.
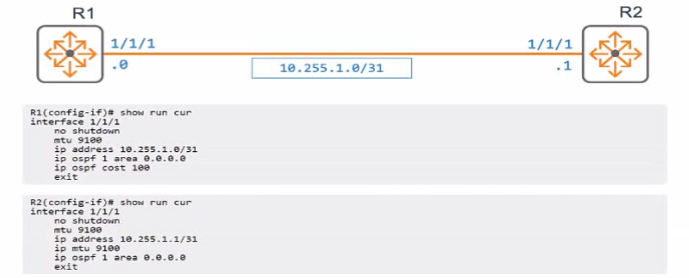
An engineer has applied the above configuration to R1 and R2 However the routers OSPF adjacency never progresses past the "EXSTART-DR" slate as shown below.
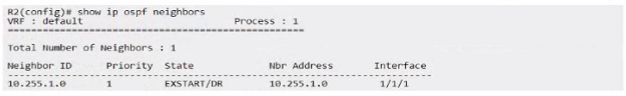
Which configuration action on either router will allow R1 and R2 to progress past the "EXSTART/DR" state?
Answer : A
In OSPF, the 'EXSTART/DR' state indicates that the routers are trying to establish an adjacency but are unable to progress. This can happen if the OSPF network type is incorrectly configured for the type of connection between the routers. Given that R1 and R2 are connected via a point-to-point link (as suggested by the /31 subnet), setting the network type to point-to-point on both routers will remove the need for DR/BDR election, which is unnecessary on a point-to-point link, and allow OSPF to progress past the 'EXSTART' state and form a full adjacency.