HP Aruba Certified Network Security Expert Written HPE6-A84 Exam Practice Test
Refer to the scenario.
A customer requires these rights for clients in the ''medical-mobile'' AOS firewall role on Aruba Mobility Controllers (MCs):
External devices should not be permitted to initiate sessions with ''medical-mobile'' clients, only send return traffic.
The line below shows the effective configuration for the role.
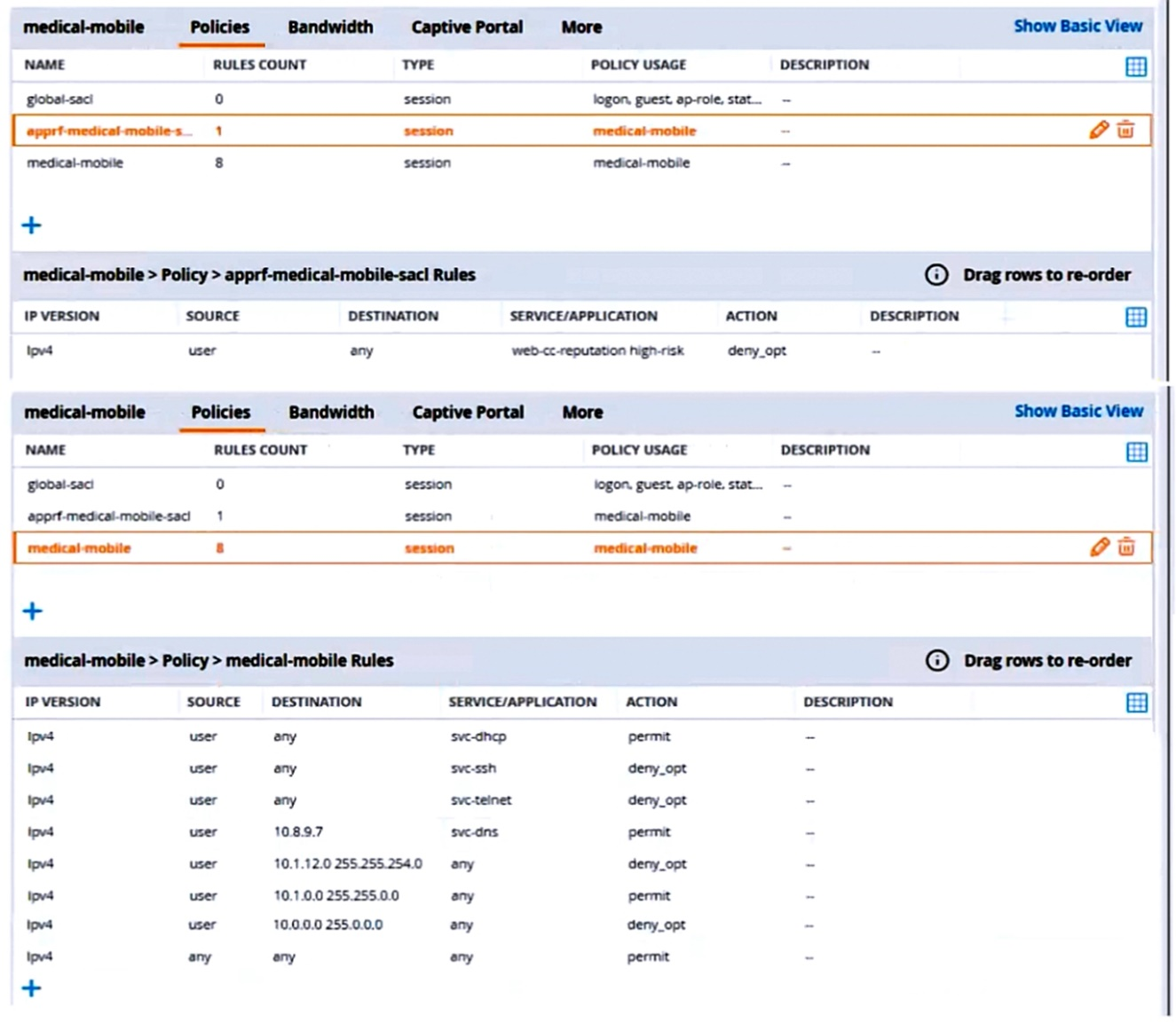
There are multiple issues with this configuration. What is one change you must make to meet the scenario requirements? (In the options, rules in a policy are referenced from top to bottom. For example, ''medical-mobile'' rule 1 is ''ipv4 any any svc-dhcp permit,'' and rule 6 is ''ipv4 any any any permit'.)
You are working with a developer to design a custom NAE script for a customer. The NAE agent should trigger an alert when ARP inspection drops packets on a VLAN. The customer wants the admins to be able to select the correct VLAN ID for the agent to monitor when they create the agent.
What should you tell the developer to do?
Answer : B
A custom NAE script is a Python script that defines the monitors, the alert-trigger logic, and the remedial actions for an NAE agent. A monitor is a URI that specifies the data source and the data type that the NAE agent should collect and analyze. For example, to monitor the ARP inspection statistics on a VLAN, the monitor URI would be something like this:

where <vlan-id> is the ID of the VLAN to be monitored.
To allow the admins to select the correct VLAN ID for the agent to monitor when they create the agent, you need to define a VLAN ID parameter in the NAE script. A parameter is a variable that can be set by the user when creating or modifying an agent. A parameter can be referenced in other parts of the script by using the syntax ${parameter-name}. For example, to define a VLAN ID parameter and reference it in the monitor URI, you would write something like this:
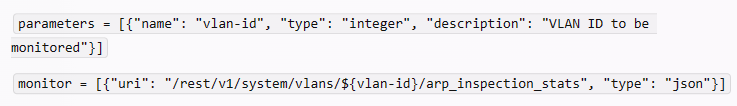
This way, when the admins create or modify the agent, they can enter the VLAN ID that they want to monitor, and the NAE script will use that value in the monitor URI.
Refer to the scenario.
An organization wants the AOS-CX switch to trigger an alert if its RADIUS server (cp.acnsxtest.local) rejects an unusual number of client authentication requests per hour. After some discussions with other Aruba admins, you are still not sure how many rejections are usual or unusual. You expect that the value could be different on each switch.
You are helping the developer understand how to develop an NAE script for this use case.
You are helping the developer find the right URI for the monitor.
Refer to the exhibit.
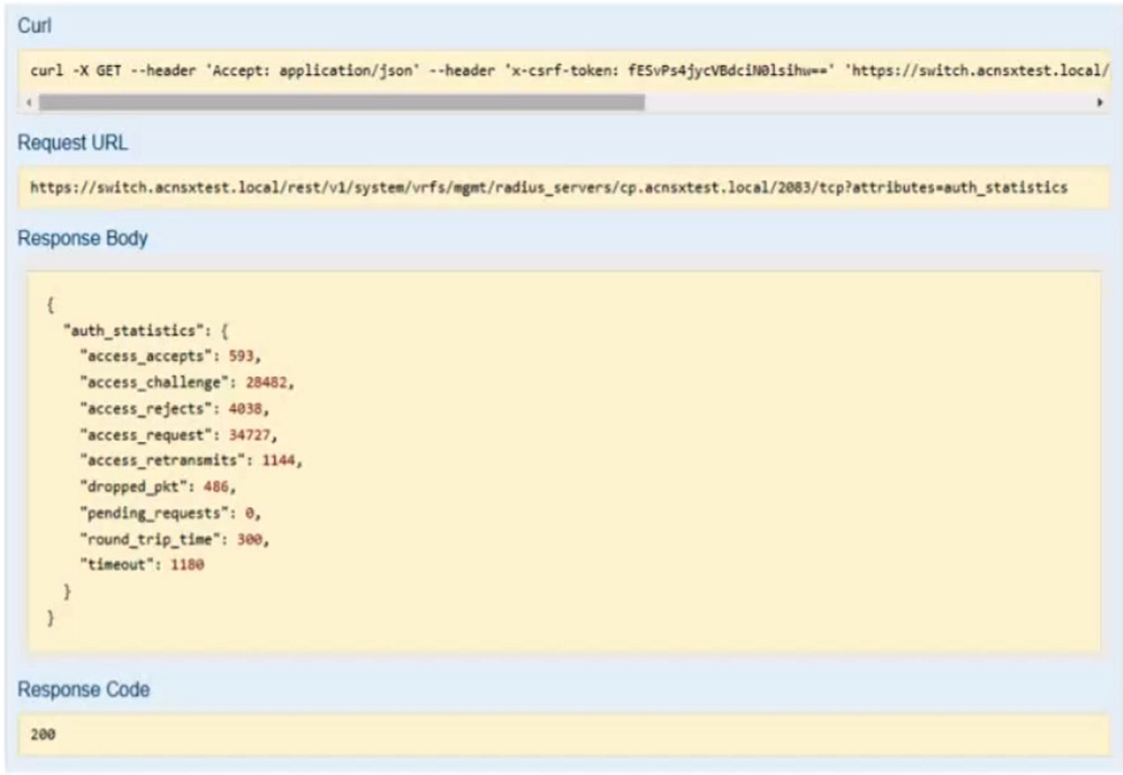
You have used the REST API reference interface to submit a test call. The results are shown in the exhibit.
Which URI should you give to the developer?
Answer : D
This is because this URI specifies the exact attribute that contains the number of access rejects from the RADIUS server, which is the information that the NAE script needs to monitor and trigger an alert.
A) /rest/v1/system/vrfs/mgmt/radius/servers/cp.acnsxtest.local/2083/tcp?attributes=authstatistics. This is not the correct URI because it returns the entire authstatistics object, which contains more information than the access rejects, such as access accepts, challenges, timeouts, etc. This might make the NAE script more complex and inefficient to parse and process the data.
B) /rest/v1/system/vrfs/mgmt/radius/servers/cp.acnsxtest.local/2083/tcp?attributes=authstatistics?attributes=access_rejects. This is not a valid URI because it has two question marks, which is a syntax error. The question mark is used to indicate the start of the query string, which can have one or more parameters separated by ampersands. The correct way to specify multiple attributes is to use a comma-separated list after the question mark, such as ?attributes=attr1,attr2,attr3.
C) /rest/v1/system/vrfs/mgmt/radius/_servers/cp.acnsxtest.local/2083/tcp. This is not a valid URI because it has an extra underscore before servers, which is a typo. The correct resource name is servers, not _servers. Moreover, this URI does not specify any attributes, which means it will return the default attributes of the RADIUS server object, such as name, port, protocol, etc., but not the authstatistics or access_rejects.
7of30
A customer has an AOS 10 architecture, which includes Aruba APs. Admins have recently enabled WIDS at the high level. They also enabled alerts and email notifications for several events, as shown in the exhibit.

Admins are complaining that they are getting so many emails that they have to ignore them, so they are going to turn off all notifications.
What is one step you could recommend trying first?
Answer : C
Therefore, one step that could be recommended to reduce the number of email notifications is to change the WIDS level to custom, and enable only the checks most likely to indicate real threats. This way, the administrators can fine-tune the WIDS settings to suit their network environment and security needs, and avoid getting flooded with irrelevant or redundant alerts. Option C is the correct answer.
Option A is incorrect because sending the email notifications directly to a specific folder and only checking the folder once a week is not a good practice for security management. This could lead to missing or ignoring important alerts that require immediate attention or action. Moreover, this does not solve the problem of getting too many emails in the first place.
Option B is incorrect because disabling email notifications for Rogue AP, but leaving the Infrastructure Attack Detected and Client Attack Detected notifications on, is not a sufficient solution. Rogue APs are unauthorized access points that can pose a serious security risk to the network, as they can be used to intercept or steal sensitive data, launch attacks, or compromise network performance. Therefore, disabling email notifications for Rogue APs could result in missing critical alerts that need to be addressed.
Option D is incorrect because disabling just the Rogue AP and Client Attack Detected alerts, as they overlap with the Infrastructure Attack Detected alert, is not a valid assumption. The Infrastructure Attack Detected alert covers a broad range of attacks that target the network infrastructure, such as deauthentication attacks, spoofing attacks, denial-of-service attacks, etc. The Rogue AP and Client Attack Detected alerts are more specific and focus on detecting and classifying rogue devices and clients that may be involved in such attacks. Therefore, disabling these alerts could result in losing valuable information about the source and nature of the attacks.
You are reviewing an endpoint entry in ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) Endpoints Repository.
What is a good sign that someone has been trying to gain unauthorized access to the network?
Answer : C
A profile conflict occurs when ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) detects a change in the device category or OS family of an endpoint that has been previously profiled. This could indicate that someone has spoofed the MAC address of a legitimate device and is trying to gain unauthorized access to the network. For example, if an endpoint that was previously profiled as a Printer suddenly shows a new profile of Computer, this could be a sign of an attack. You can find more information about profile conflicts and how to resolve them in the ClearPass Policy Manager User Guide1. The other options are not necessarily signs of unauthorized access, as they could have other explanations. For example, multiple DHCP options under the fingerprints could indicate that the device has connected to different networks or subnets, an Unknown status could indicate that the device has not been authenticated yet, and a lack of hostname or a random hostname could indicate that the device has not been configured properly or has been reset to factory settings.
How does Aruba Central handle security for site-to-site connections between AOS 10 gateways?
Answer : B
A customer has an AOS 10-based mobility solution, which authenticates clients to Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM). The customer has some wireless devices that support WPA2 in personal mode only.
How can you meet these devices' needs but improve security?
Answer : A
MPSK (Multi Pre-Shared Key) is a feature that allows assigning different pre-shared keys (PSKs) to different devices or groups of devices on the same WLAN. MPSK improves security over WPA2 in personal mode, which uses a single PSK for all devices on the WLAN. With MPSK, you can create and manage multiple PSKs, each with its own role, policy, and expiration date. You can also revoke or change a PSK for a specific device or group without affecting other devices on the WLAN. MPSK is compatible with devices that support WPA2 in personal mode only, as they do not need to support any additional protocols or certificates.
To use MPSK on the WLAN to which the devices connect, you need to enable MPSK in the WLAN settings and configure the PSKs in Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM). You can find more information about how to configure MPSK in the [Configuring Multi Pre-Shared Key - Aruba] page and the [ClearPass Policy Manager User Guide] . The other options are not correct because they either do not improve security or are not applicable for devices that support WPA2 in personal mode only. For example, configuring WIDS policies that apply extra monitoring to these particular devices would not prevent them from being compromised or spoofed, but rather detect and mitigate potential attacks. Connecting these devices to the same WLAN to which 802.1X-capable clients connect, using MAC-Auth fallback, would not provide strong authentication or encryption, as MAC addresses can be easily spoofed or captured. Enabling dynamic authorization (RFC 3576) in the AAA profile for the devices would not affect the authentication process, but rather allow CPPM to change the attributes or status of a user session on the controller without requiring re-authentication.