HashiCorp HCVA0-003 HashiCorp Certified: Vault Associate (003) Exam Practice Test
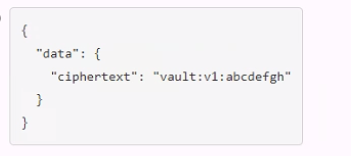
A user issues the following cURL command to encrypt data using the transit engine and the Vault AP:
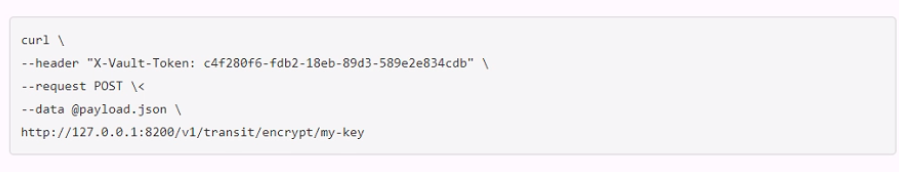
Which payload.json file has the correct contents?
A.
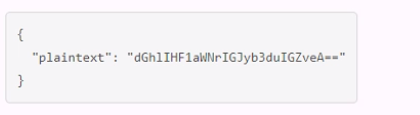
B.
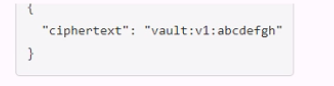
C.
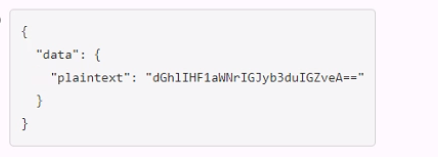
D.
When an auth method is disabled all users authenticated via that method lose access.
A developer mistakenly committed code that contained AWS S3 credentials into a public repository. You have been tasked with revoking the AWS S3 credential that was in the code. This credential was created using Vault's AWS secrets engine and the developer received the following output when requesting a credential from Vault.
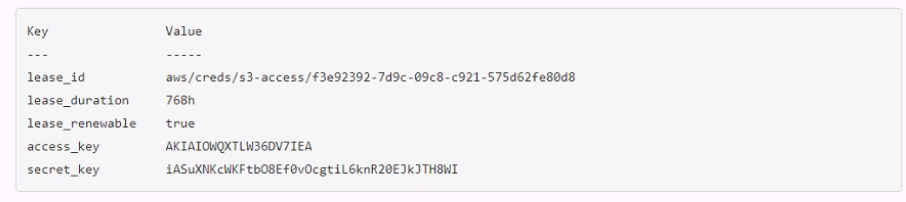
Which Vault command will revoke the lease and remove the credential from AWS?
Answer : A
You are performing a high number of authentications in a short amount of time. You're experiencing slow throughput for token generation. How would you solve this problem?
True or False? Performing a rekey operation using the vault operator rekey command creates new unseal/recovery keys as well as a new root key?
Answer : B
Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth
False. The vault operator rekey command updates unseal/recovery keys, not the master key (often confused with ''root key''). The Vault documentation states:
'The operator rekey command generates a new set of unseal keys. This can optionally change the total number of key shares or the required threshold of those key shares to reconstruct the master key. This operation is zero downtime, but it requires that Vault is unsealed and a quorum of existing unseal keys are provided.'
--- Vault Commands: operator rekey
B: Correct. Only unseal keys are recreated:
'When performing a rekey operation using the vault operator rekey command, new unseal/recovery keys are generated, but the root key remains the same.'
--- Vault Commands: operator rekey
A: Incorrect; the master key persists.
Vault Commands: operator rekey
Your organization audited an essential application and found it isn't securely storing dat
a. For added security, auditors recommended encrypting all data before storing it in a backend database, and the application server should not store encryption keys locally. Which secrets engine meets these requirements?
Answer : C
Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth
The Transit secrets engine encrypts data without local key storage. The Vault documentation states:
'The Transit secrets engine allows you to send cleartext data to Vault to be encrypted. Vault will encrypt the data with the referenced encryption key, which is stored locally, and returns the ciphertext to the application. Although the encryption keys in the Transit secrets engine are exportable, they are generally kept in Vault.'
--- Transit Tutorial
C: Correct. Meets encryption and key security needs:
'It allows applications to encrypt data before storing it in a backend database and decrypt it when needed, without storing encryption keys locally.'
--- Vault Secrets: Transit
A: PKI is for certificates.
B: SSH is for SSH credentials.
D: Cubbyhole is for temporary storage.
Transit Tutorial
Vault Secrets: Transit