Google Associate Cloud Engineer Exam Practice Test
Your company requires that Google Cloud products are created with a specific configuration to comply with your company's security policies You need to implement a mechanism that will allow software engineers at your company to deploy and update Google Cloud products in a preconfigured and approved manner. What should you do?
Answer : C
You need to extract text from audio files by using the Speech-to-Text API. The audio files are pushed to a Cloud Storage bucket. You need to implement a fully managed, serverless compute solution that requires authentication and aligns with Google-recommended practices. You want to automate the call to the API by submitting each file to the API as the audio file arrives in the bucket. What should you do?
Answer : B
Your manager asks you to deploy a workload to a Kubernetes cluster. You are not sure of the workloads resource requirements or how the requirements might vary depending on usage patterns, external dependencies, or other factors. You need a solution that makes cost-effective recommendations regarding CPU and memory requirements, and allows the workload to function consistently in any situation. You want to follow Google-recommended practices. What should you do?
Answer : D
Your customer wants you to create a secure website with autoscaling based on the compute instance CPU load. You want to enhance performance by storing static content in Cloud Storage. Which resources are needed to distribute the user traffic?
Answer : C
An external HTTP(S) load balancer is a Google-recommended solution for distributing web traffic across multiple regions and zones, and providing high availability, scalability, and security for web applications. It supports both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, and can handle SSL/TLS termination and encryption. It also integrates with Cloud CDN, Cloud Armor, and Cloud Identity-Aware Proxy for enhanced performance and protection. A managed instance group (MIG) can be used as a backend service for the HTTP(S) load balancer, and can automatically scale the number of VM instances based on the CPU load. A Cloud Storage bucket can also be used as a backend service for the HTTP(S) load balancer, and can serve static content such as images, videos, or HTML files. A URL map can be used to route requests to different backend services based on the path or host of the request. For example, a URL map can send requests for/static/*to the Cloud Storage bucket, and requests for/dynamic/*to the MIG. A managed SSL certificate can be used to secure the connection between the clients and the load balancer, and can be automatically provisioned and renewed by Google.
A is incorrect because an internal HTTP(S) load balancer is only visible within a VPC network, and not to the public internet. It is used for internal applications that need to communicate with other internal services. Identity-Aware Proxy is a service that provides secure access to web applications without using a VPN. It is not a load balancer, and it does not distribute user traffic.
B is incorrect because installing HTTPS certificates on the instance is not necessary, as the HTTP(S) load balancer can handle SSL/TLS termination and encryption. It is also more complex and less secure to manage the certificates on the instance level, as they need to be updated and synchronized across multiple instances.
D is incorrect because an external network load balancer is a TCP/UDP load balancer that operates at the network layer. It is not suitable for web applications that use HTTP(S) protocols, as it does not support SSL/TLS termination and encryption, URL maps, or Cloud Storage backends. It is also less efficient and scalable to forward the requests to the Cloud Storage from the web servers, as it adds an extra hop and latency.
HTTP(S) Load Balancing documentation
Setting up HTTP(S) Load Balancing with Cloud Storage
You want to host your video encoding software on Compute Engine. Your user base is growing rapidly, and users need to be able 3 to encode their videos at any time without interruption or CPU limitations. You must ensure that your encoding solution is highly available, and you want to follow Google-recommended practices to automate operations. What should you do?
Answer : D
Instance groups are collections of virtual machine (VM) instances that you can manage as a single entity. Instance groups can help you simplify the management of multiple instances, reduce operational costs, and improve the availability and performance of your applications. Instance groups support autoscaling, which automatically adds or removes instances from the group based on increases or decreases in load. Autoscaling helps your applications gracefully handle increases in traffic and reduces cost when the need for resources is lower. You can set the autoscaling policy based on CPU utilization, load balancing capacity, Cloud Monitoring metrics, or a queue-based workload. In this case, since the video encoding software is CPU-intensive, setting the autoscaling based on CPU utilization is the best option to ensure high availability and optimal performance.Reference:
Autoscaling groups of instances
You used the gcloud container clusters command to create two Google Cloud Kubernetes (GKE) clusters prod-cluster and dev-cluster.
* prod-cluster is a standard cluster.
* dev-cluster is an auto-pilot duster.
When you run the Kubect1 get nodes command, you only see the nodes from prod-cluster Which commands should you run to check the node status for dev-cluster?
A.
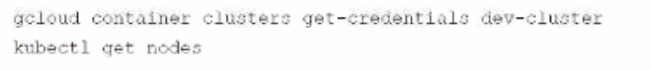
B.

C.

D.

Answer : C
Your company requires all developers to have the same permissions, regardless of the Google Cloud project they are working on. Your company's security policy also restricts developer permissions to Compute Engine. Cloud Functions, and Cloud SQL. You want to implement the security policy with minimal effort. What should you do?