Fortinet NSE8_812 Fortinet NSE 8 - Written Exam Practice Test
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a FortiGate configuration snippet.

A customer in Costa Rica has a FortiGate with SD-WAN configured to use a VPN connection to the United States to browse the internet using a public IP from that country. They would like to enable the SD-WAN rule using a webhook.
Which configuration must be added to the FortiGate, and which type of HTTP request must be used to accomplish this? (Choose two.)
A.
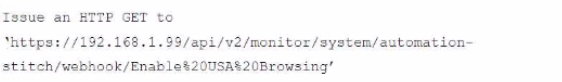
B.

C.
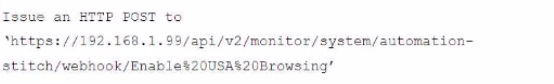
D.

Answer : A, B
You are responsible for recommending an adapter type for NICs on a FortiGate VM that will run on an ESXi Hypervisor. Your recommendation must consider performance as the main concern, cost is not a factor. Which adapter type for the NICs will you recommend?
Refer to the exhibits.
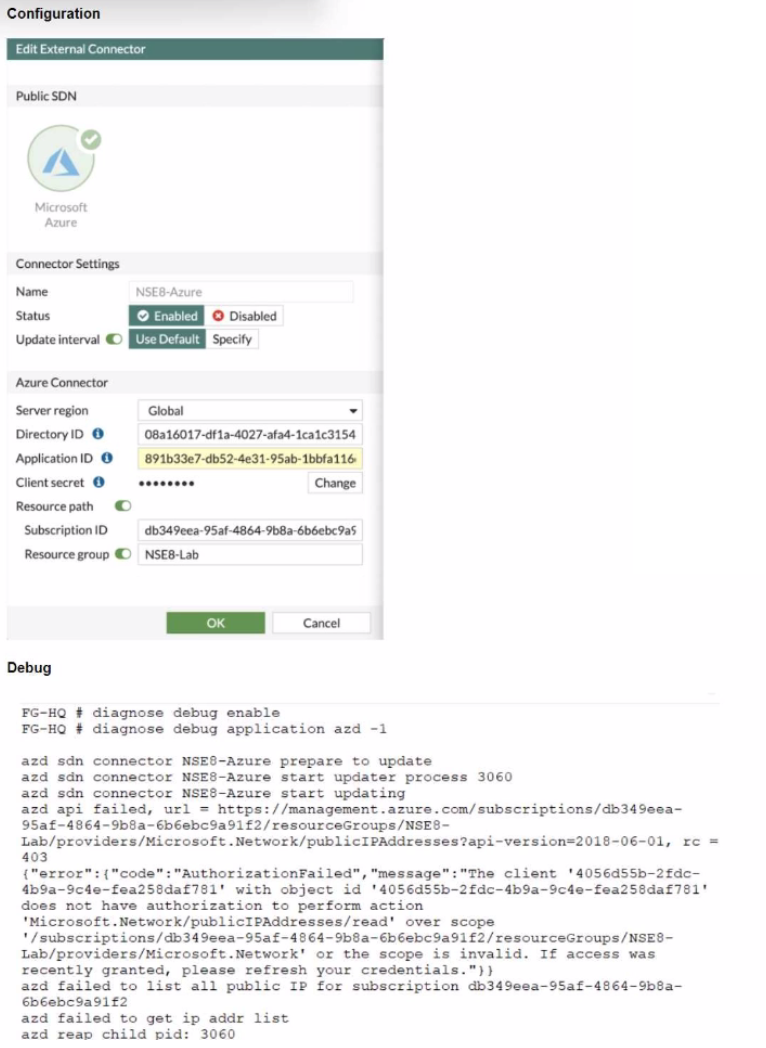
The exhibits show the configuration and debug output from a FortiGate Public SDN Connector.
What is a possible reason for this dynamic address object to be empty?
Answer : C
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit A
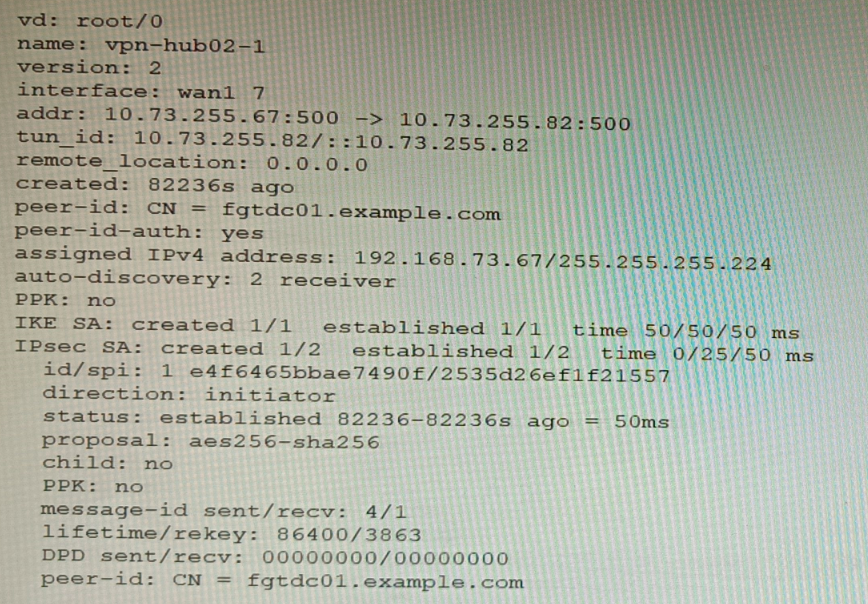
Exhibit B
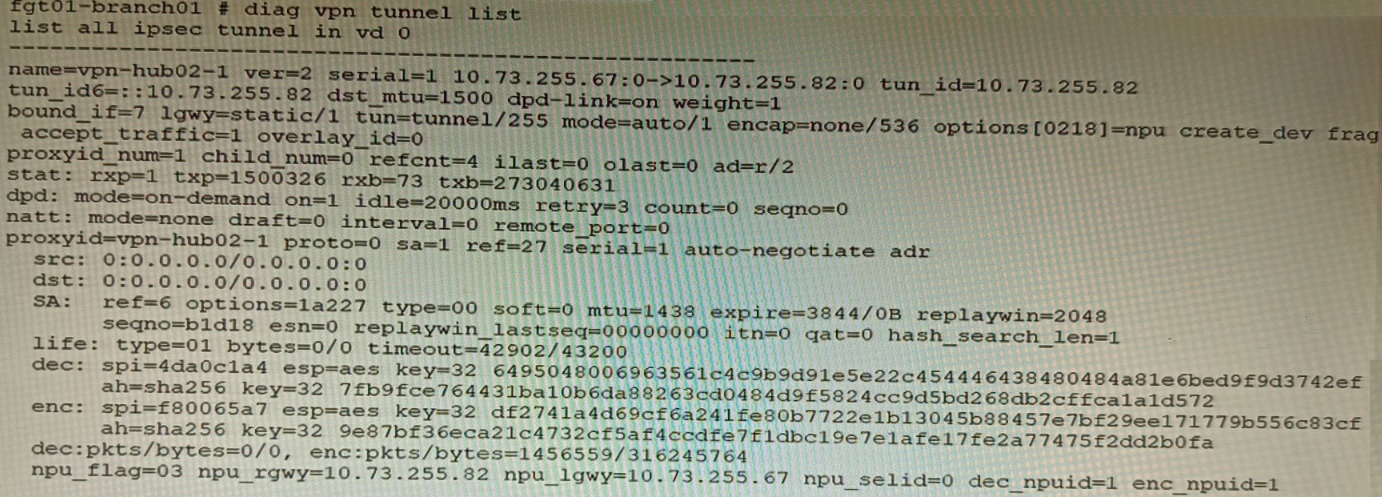
Exhibit C
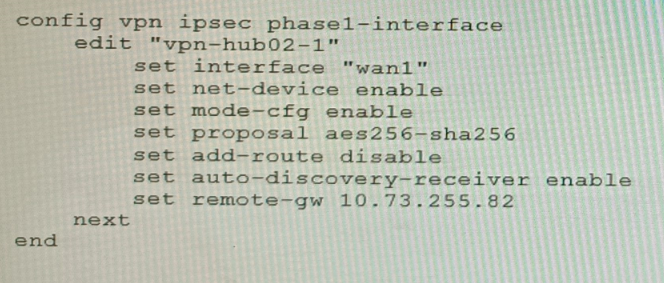
A customer is trying to set up a VPN with a FortiGate, but they do not have a backup of the configuration. Output during a troubleshooting session is shown in the exhibits A and B and a baseline VPN configuration is shown in Exhibit C Referring to the exhibits, which configuration will restore VPN connectivity?
A)
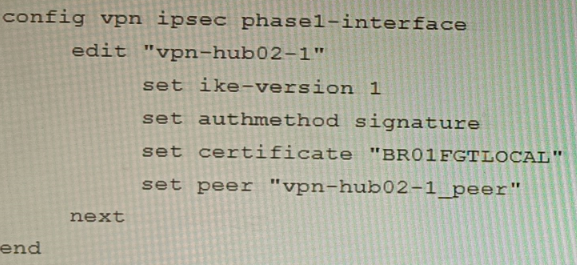
B)
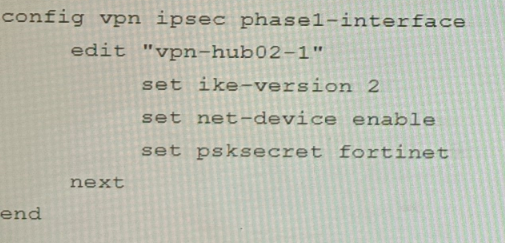
C)

D)

Answer : C
The output in Exhibit A shows that the VPN tunnel is not established because the peer IP address is incorrect. The output in Exhibit B shows that the peer IP address is 192.168.1.100, but the baseline VPN configuration in Exhibit C shows that the peer IP address should be 192.168.1.101.
To restore VPN connectivity, you need to change the peer IP address in the VPN tunnel configuration to 192.168.1.101. The correct configuration is shown below:
config vpn ipsec phase1-interface
edit 'wan'
set peer-ip 192.168.1.101
set peer-id 192.168.1.101
set dhgrp 1
set auth-mode psk
set psk SECRET_PSK
next
end
Option A is incorrect because it does not change the peer IP address. Option B is incorrect because it changes the peer IP address to 192.168.1.100, which is the incorrect IP address. Option D is incorrect because it does not include the necessary configuration for the VPN tunnel.
Refer to the exhibits.
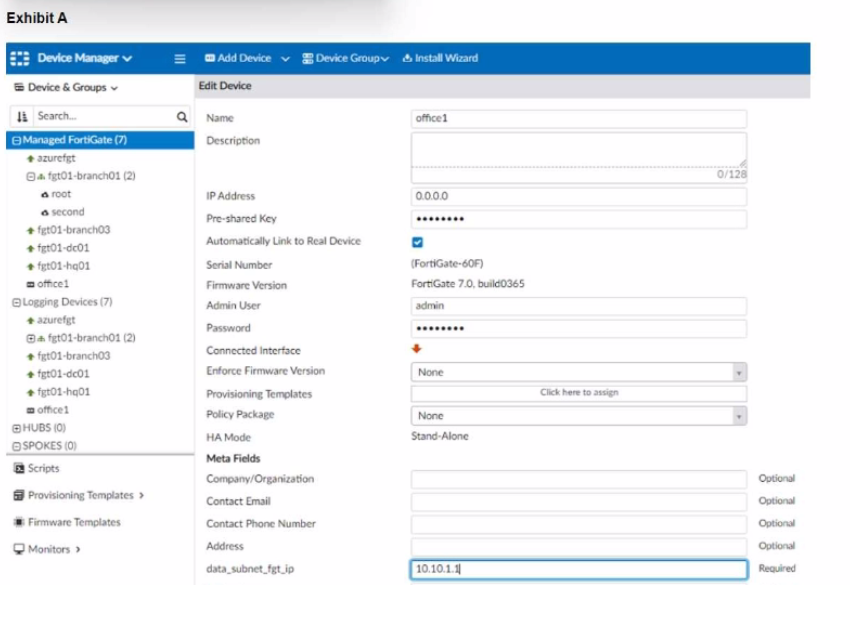
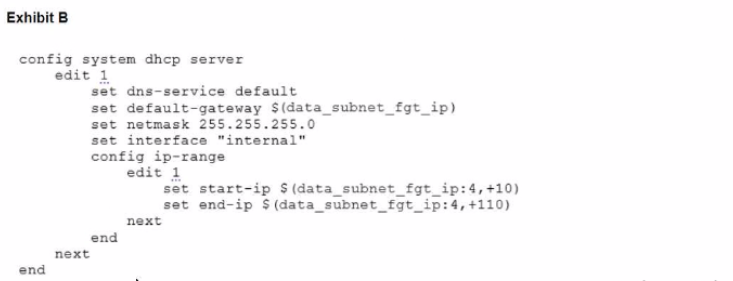
To facilitate a more efficient roll out of FortiGate devices, you are tasked with using meta fields with the CLI Template to configure the DHCP server on the "office1" FortiGate.
Given this scenario, what would be the output of the config ip-range section on the CLI Template?
A.
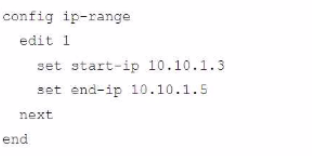
B.
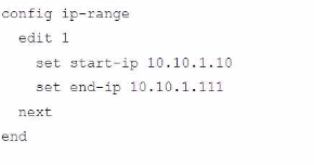
C.

D.

Answer : A
Refer to the exhibits.
The exhibits show a diagram of a requested topology and the base IPsec configuration.
A customer asks you to configure ADVPN via two internet underlays. The requirement is that you use one interface with a single IP address on DC FortiGate.
In this scenario, which feature should be implemented to achieve this requirement?
Answer : A
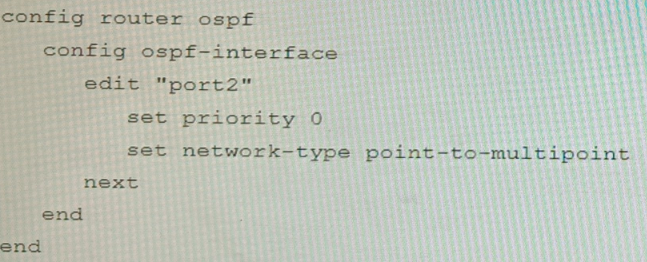
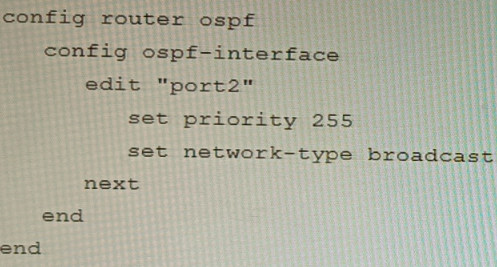
Refer to the exhibit.
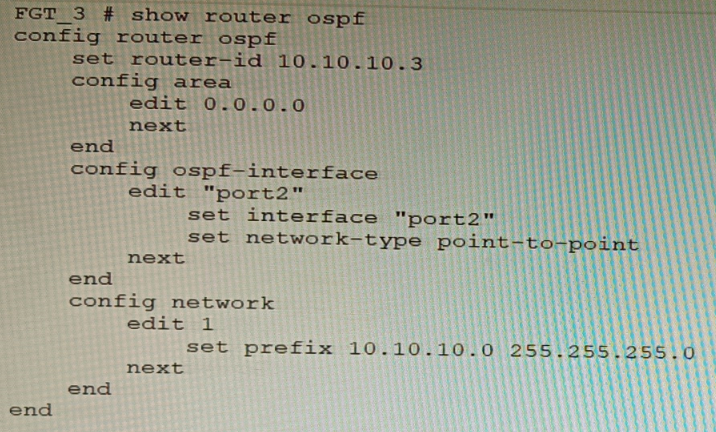
You are operating an internal network with multiple OSPF routers on the same LAN segment. FGT_3 needs to be added to the OSPF network and has the configuration shown in the exhibit. FGT_3 is not establishing any OSPF connection.
What needs to be changed to the configuration to make sure FGT_3 will establish OSPF neighbors without affecting the DR/BDR election?
A)
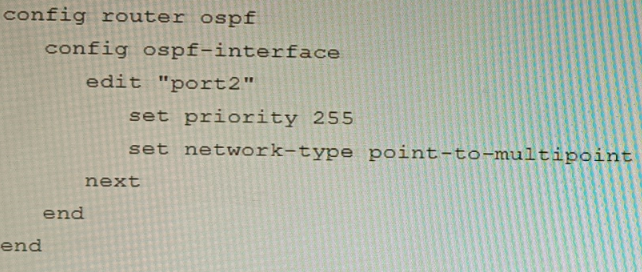
B)
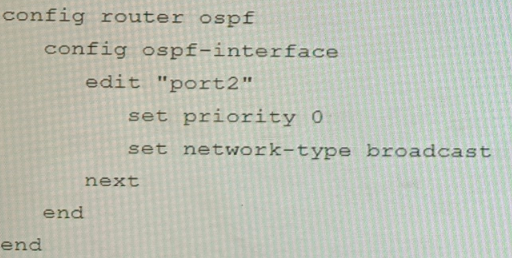
C)
D)