Fortinet NSE 7 - Public Cloud Security 7.2 NSE7_PBC-7.2 Exam Practice Test
You are adding a new spoke to the existing transit VPC environment using the AWS Cloud Formation template. Which two components must you use for this deployment? (Choose two.)
Answer : C, D
When using an AWS CloudFormation template to add a new spoke to an existing transit VPC environment, the necessary components are:
The BGPASN value used for the transit VPC (Option C): BGP Autonomous System Number (ASN) is required for setting up BGP routing between the transit VPC and the new spoke. This number uniquely identifies the system in BGP routing and is crucial for correct routing and avoiding routing conflicts.
The tag value of the spoke (Option D): Tags in AWS are used to identify and manage resources. The tag value assigned to a spoke VPC helps in organizing, managing, and locating the VPC within the larger AWS environment. Tags are essential for automation scripts and policies that depend on specific identifiers to apply configurations or rules.
What are two main features in Amazon Web Services (AWS) network access control lists (ACLs)? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, C
The other options are incorrect because:
Refer to the exhibit
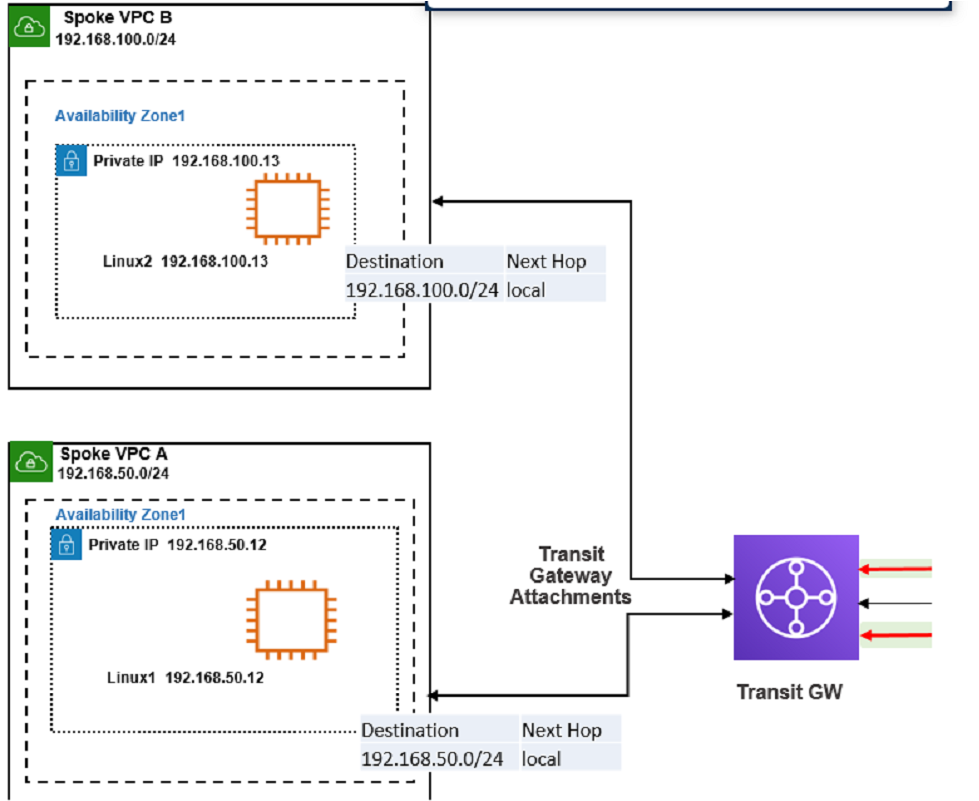
The exhibit shows a customer deployment of two Linux instances and their main routing table in Amazon Web Services (AWS). The customer also created a Transit Gateway (TGW) and two attachments
Which two steps are required to route traffic from Linux instances to the TGWQ (Choose two.)
Answer : A, B
According to the AWS documentation for Transit Gateway, a Transit Gateway is a network transit hub that connects VPCs and on-premises networks. To route traffic from Linux instances to the TGW, you need to do the following steps:
In the TGW route table, associate two attachments. An attachment is a resource that connects a VPC or VPN to a Transit Gateway. By associating the attachments to the TGW route table, you enable the TGW to route traffic between the VPCs and the VPN.
In the main subnet routing table in VPC A and B, add a new route with destination 0_0.0.0/0, next hop TGW. This route directs all traffic from the Linux instances to the TGW, which can then forward it to the appropriate destination based on the TGW route table.
The other options are incorrect because:
In the TGW route table, adding route propagation to 192.168.0 0/16 is not necessary, as this is already the default route for the TGW. Route propagation allows you to automatically propagate routes from your VPC or VPN to your TGW route table.
In the main subnet routing table in VPC A and B, adding a new route with destination 0_0.0.0/0, next hop Internet gateway (IGW) is not correct, as this would bypass the TGW and send all traffic directly to the internet. An IGW is a VPC component that enables communication between instances in your VPC and the internet.
: [Transit Gateways - Amazon Virtual Private Cloud]
Refer to the exhibit
An administrator deployed a FortiGate-VM in a high availability (HA)
(active/passive) architecture in Amazon Web Services (AWS) using Terraform
for testing purposes. At the same time, the administrator deployed a single
Linux server using AWS Marketplace
Which two options are available for the administrator to delete all the resources
created in this test? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, D
The other options are incorrect because:
Refer to the exhibit

You are tasked with deploying a webserver and FortiGate VMS in AWS_ You are using Terraform to automate the process
Which two important details should you know about the Terraform files? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, B
The other options are incorrect because:
After the deployment, Terraform output values are not visible only through AWS CloudShell. You can access them from any shell or terminal where you have Terraform installed and configured with your AWS credentials.
Output Values - Configuration Language | Terraform - HashiCorp Developer
Command: output - Terraform by HashiCorp
Input Variables - Configuration Language | Terraform - HashiCorp Developer
Configuration Language | Terraform - HashiCorp Developer
Which statement about immutable infrastructure in automation is true?
Answer : A
The statement that best describes the concept of immutable infrastructure in the context of automation is:
A . It is the practice of deploying a new server for every configuration change.
Immutable Infrastructure Concept: This approach to infrastructure management involves replacing servers or components entirely rather than making changes to existing configurations once they are deployed. When a change is needed, a new server instance is provisioned with the desired configuration and the old one is decommissioned after the new one is successfully deployed and tested.
Benefits: Immutable infrastructure minimizes the risks associated with in-place updates, such as inconsistencies or failures due to configuration drift. It enhances reliability and predictability by ensuring that the deployed environment matches exactly what was tested in staging. This practice is particularly aligned with modern deployment strategies like blue/green or canary deployments.
You are adding more spoke VPCs to an existing hub and spoke topology Your goal is to finish this task in the minimum amount of time without making errors.
Which Amazon AWS services must you subscribe to accomplish your goal?
Answer : D
The correct answer is D. CloudWatch and S3.
CloudWatch: A monitoring and observability service that collects and processes events from various AWS resources, including Transit Gateway attachments and route tables.
S3: A scalable object storage service that can store the configuration files and logs generated by the Lambda function.
The other AWS services mentioned in the options are not required for this task. GuardDuty is a threat detection service that monitors for malicious and unauthorized behavior to help protect AWS accounts and workloads. WAF is a web application firewall that helps protect web applications from common web exploits. Inspector is a security assessment service that helps improve the security and compliance of applications deployed on AWS. DynamoDB is a fast and flexible NoSQL database service that can store various types of data.
1: GitHub - fortinet/aws-lambda-tgw