Fortinet NSE7_NST-7.2 Fortinet NSE 7 - Network Security 7.2 Support Engineer Exam Practice Test
What are two functions of automation stitches? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, C
Automation Stitches Overview:
Automation stitches in FortiOS allow administrators to automate responses to specific events, such as running diagnostic commands or taking corrective actions when certain thresholds are exceeded.
Diagnostic Commands and Alerts:
Automation stitches can be configured to run diagnostic commands and attach the results to email alerts. This is useful for monitoring and troubleshooting purposes, particularly when CPU or memory usage exceeds set thresholds.
Sequential Execution with Parameters:
When actions are executed sequentially, each action can take parameters from the previous action as input. This enables more complex workflows and automation sequences where the output of one action influences the next.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the output of diagnose sys session stat. Which statement about the output shown in the exhibit is correct?
Answer : C
Session Table Overview:
The session table in FortiOS tracks all active and pending sessions. It includes details like the type of session (TCP, UDP, etc.), status, and statistics.
Interpreting the Exhibit:
The exhibit from the diagnose sys session stat command shows detailed session statistics.
The specific value indicating '166 TCP sessions waiting to complete the three-way handshake' reflects the number of sessions that have initiated but not yet completed the TCP three-way handshake process (SYN, SYN-ACK, ACK).
Fortinet Documentation: Understanding and troubleshooting session tables (Hammertux).
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the omitted output of FortiOS kernel slabs.
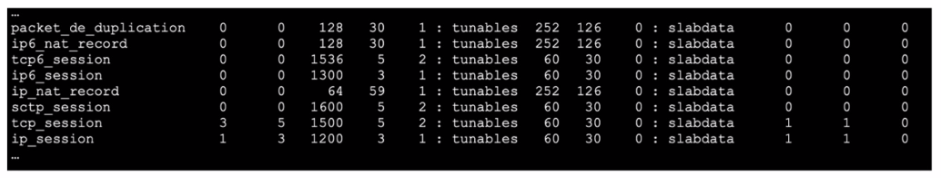
Which statement is true?
Answer : B
Kernel Slabs Overview:
The slab allocator in the Linux kernel is used for efficient memory management. It groups objects of the same type into caches, which are divided into slabs.
Each slab contains multiple objects and helps to minimize fragmentation and enhance memory allocation efficiency.
Interpreting the Exhibit:
The exhibit shows output related to various kernel slab caches.
The line for ip6_session indicates that there are 1300 kB allocated for this slab, which means the total memory size allocated for IPv6 session objects in the kernel is 1300 kB.
Linux Kernel Documentation: Slab Allocator details (Hammertux).
Exhibit.
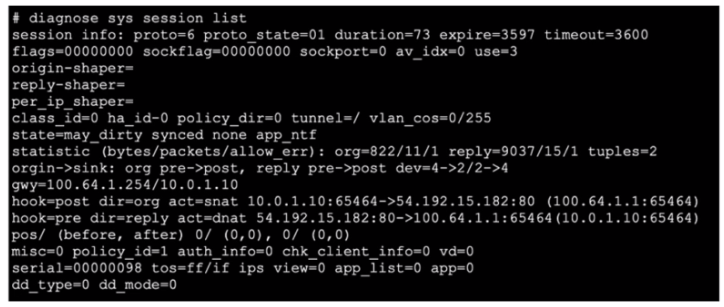
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the output of diagnose sys session list.
If the HA ID for the primary device is 0. what happens if the primary fails and the secondary becomes the primary?
Answer : C
Session Synchronization:
FortiGate HA (High Availability) ensures that active sessions are synchronized between the primary and secondary devices. This synchronization allows for seamless failover and continuity of sessions.
Handling NAT Sessions:
The session in the exhibit has NAT applied, as indicated by the hook=post dir=org act=snat entry. FortiGate's HA setup is designed to handle such sessions, ensuring that traffic continues without interruption during failover.
Session Preservation:
Even with the presence of NAT, the session state is preserved across the HA devices. This means that ongoing sessions do not require re-establishment by the client, thus providing a seamless experience.
Fortinet Documentation: HA session synchronization and failover
Fortinet Community: Understanding session synchronization in FortiGate HA
There are four exchanges during IKEv2 negotiation.
Which sequence is correct?
Answer : D
IKE_SA_INIT:
This is the first exchange in IKEv2. It establishes a secure, authenticated channel between peers and negotiates cryptographic algorithms and keys.
IKE_Auth:
The second exchange authenticates the IKE SA (Security Association) using the previously negotiated keys and algorithms. This exchange also establishes the first IPsec SA.
Create_CHILD_SA:
This exchange creates additional IPsec SAs after the initial authentication. It can also be used to rekey existing IPsec SAs to maintain security.
Informational:
This is a generic exchange used for various purposes such as error notification, deletion of SAs, and other control messages.
Fortinet Community: IKEv2 packet exchanges and troubleshooting
Fortinet Documentation: IPsec VPN Concepts
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a truncated output of a real-time LDAP debug.
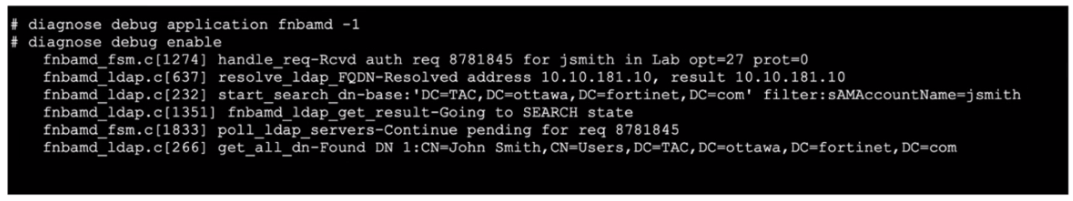
What two conclusions can you draw from the output? (Choose two.)
Answer : C, D
LDAP Authentication Process:
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) authentication involves several steps: Bind Request, Search Request, and Bind Response.
The Bind Request is used to authenticate the client to the LDAP server.
The Search Request is used to find the directory entry that matches the provided criteria.
Analyzing the Exhibit:
The exhibit shows a real-time LDAP debug output.
The debug log includes a successful resolution of the LDAP FQDN, indicating that the LDAP server was reached.
The debug log also shows the start of a search using the distinguished name (DN) base and a filter to locate the user jsmith.
Conclusion:
Since FortiOS successfully resolved the LDAP server and initiated a search for the user jsmith, it indicates that the LDAP server was located, and the search request was performed.
Fortinet Community: Understanding LDAP authentication steps and troubleshooting (Fortinet Docs).
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the output of get router info ospf neighbor.
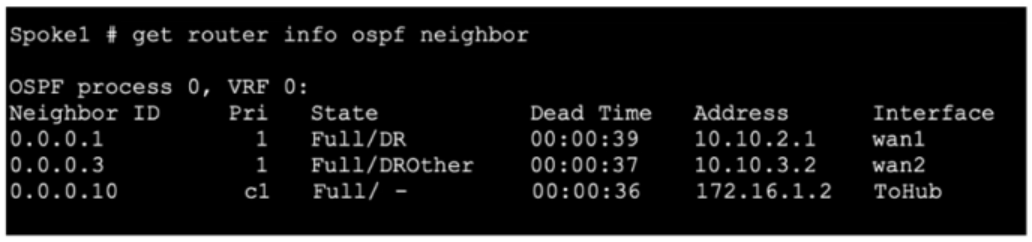
What can you conclude from the command output?
Answer : A
Understanding OSPF Roles:
In OSPF (Open Shortest Path First), routers can have different roles: Designated Router (DR), Backup Designated Router (BDR), and DROther. These roles help manage and optimize the OSPF network traffic.
DR and BDR are elected to minimize the number of adjacencies and reduce the amount of routing information exchange.
DROther routers are neither DR nor BDR but can still participate in the OSPF network by maintaining adjacencies with DR and BDR.
Analyzing the Exhibit:
The exhibit shows the OSPF neighbor states for the local FortiGate.
Neighbor ID 0.0.0.1 is in the state Full/DR (Designated Router).
Neighbor ID 0.0.0.3 is in the state Full/DROther (DROther).
Neighbor ID 0.0.0.10 has no specific designation, implying it is neither DR nor BDR.
Conclusion:
Since the local FortiGate shows neighbors in Full/DR and Full/DROther states and itself does not have a state of DROther, it can be concluded that the local FortiGate is not a DROther.
Fortinet Documentation: OSPF neighbor states and elections (Fortinet Docs).