Fortinet NSE7_LED-7.0 Fortinet NSE 7 - LAN Edge 7.0 Exam Practice Test
Which CLI command should an administrator use to view the certificate verification process in real time?
Answer : A
According to the FortiOS CLI Reference Guide, ''The diagnose debug application foauthd command enables debugging of certificate verification process in real time.'' Therefore, option A is true because it describes the CLI command that an administrator should use to view the certificate verification process in real time. Option B is false because diagnose debug application radiusd -1 enables debugging of RADIUS authentication process, not certificate verification process. Option C is false because diagnose debug application authd -1 enables debugging of authentication daemon process, not certificate verification process. Option D is false because diagnose debug application fnbamd -1 enables debugging of FSSO daemon process, not certificate verification process.
Refer to the exhibit.

By default FortiOS creates the following DHCP server scope for the FortiLink interface as shown in the exhibit
What is the objective of the vci-string setting?
Answer : C
According to the exhibit, the DHCP server scope for the FortiLink interface has a vci-string setting with the value ''Cisco AP c2700''. This setting is used to match the vendor class identifier (VCI) of the DHCP clients that request an IP address from the DHCP server. The VCI is a text string that uniquely identifies a type of vendor device. Therefore, option C is true because the vci-string setting restricts the IP address assignment to FortiSwitch and FortiExtender devices, which use the VCI ''Cisco AP c2700''. Option A is false because the vci-string setting does not ignore DHCP requests coming from FortiSwitch and FortiExtender devices, but rather accepts them. Option B is false because the vci-string setting does not reserve IP addresses for FortiSwitch and FortiExtender devices, but rather assigns them dynamically. Option D is false because the vci-string setting does not restrict the IP address assignment to devices that have FortiSwitch or FortiExtender as their hostname, but rather to devices that have ''Cisco AP c2700'' as their VCI.
You are investigating a report of poor wireless performance in a network that you manage. The issue is related to an AP interface in the 5 GHz range You are monitoring the channel utilization over time.
What is the recommended maximum utilization value that an interface should not exceed?
Answer : D
According to the FortiAP Configuration Guide, ''Channel utilization measures how busy a channel is over a given period of time. It includes both Wi-Fi and non-Wi-Fi interference sources. A high channel utilization indicates a congested channel and can result in poor wireless performance. The recommended maximum utilization value that an interface should not exceed is 65%.'' Therefore, option D is true because it gives the recommended maximum utilization value for an interface in the 5 GHz range. Options A, B, and C are false because they give higher utilization values that can cause poor wireless performance.
: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiap/7.0.0/configuration-guide/734537/wireless-radio-settings#channel-utilization
An administrator is testing the connectivity for a new VLAN The devices in the VLAN are connected to a FortiSwitch device that is managed by FortiGate Quarantine is disabled on FortiGate
While testing the administrator noticed that devices can ping FortiGate and FortiGate can ping the devices The administrator also noticed that inter-VLAN communication works However intra-VLAN communication does not work
Which scenario is likely to cause this issue?
Answer : C
According to the scenario, the devices in the VLAN are connected to a FortiSwitch device that is managed by FortiGate. Quarantine is disabled on FortiGate, which means that the devices are not blocked by any security policy. The devices can ping FortiGate and FortiGate can ping the devices, which means that the IP connectivity is working. Inter-VLAN communication works, which means that the routing between VLANs is working. However, intra-VLAN communication does not work, which means that the switching within the VLAN is not working. Therefore, option C is true because the FortiSwitch MAC address table is missing entries, which means that the FortiSwitch does not know how to forward frames to the destination MAC addresses within the VLAN. Option A is false because access VLAN is enabled on the VLAN, which means that the VLAN ID is added to the frames on ingress and removed on egress. This does not affect intra-VLAN communication. Option B is false because the native VLAN configured on the ports is incorrect, which means that the frames on the native VLAN are not tagged with a VLAN ID. This does not affect intra-VLAN communication. Option D is false because the FortiGate ARP table is missing entries, which means that FortiGate does not know how to map IP addresses to MAC addresses. This does not affect intra-VLAN communication.
Refer to the exhibit.
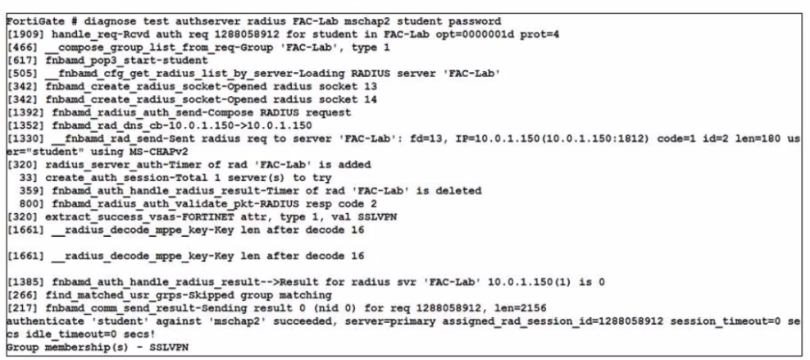
Examine the debug output shown in the exhibit
Which two statements about the RADIUS debug output are true'' (Choose two)
Answer : A, D
According to the exhibit, the debug output shows a RADIUS debug output from FortiGate. The output shows that FortiGate sent a RADIUS Access-Request packet to FortiAuthenticator with the username student and received a RADIUS Access-Accept packet from FortiAuthenticator with a Class attribute containing SSLVPN. Therefore, option A is true because it indicates that the user student belongs to the SSLVPN group on FortiAuthenticator. The output also shows that FortiGate used MSCHAP as the authentication method and received a MS-MPPE-Send-Key and a MS-MPPE-Recv-Key from FortiAuthenticator. Therefore, option D is true because it indicates that user authentication succeeded using MSCHAP. Option B is false because user authentication did not fail, but rather succeeded. Option C is false because FortiAuthenticator did not send a vendor-specific attribute in the RADIUS response, but rather standard attributes defined by RFCs.
Refer to the exhibit.

Refer to the exhibit showing a network topology and SSID settings.
FortiGate is configured to use an external captive portal However wireless users are not able to see the captive portal login page
Which configuration change should the administrator make to fix the problem?
Answer : B
According to the exhibit, the network topology and SSID settings show that FortiGate is configured to use an external captive portal hosted on FortiAuthenticator, which is connected to a Windows AD server for user authentication. However, wireless users are not able to see the captive portal login page, which means that they are not redirected to the external captive portal URL. Therefore, option B is true because adding the FortiAuthenticator and WindowsAD address objects as exempt destinations services will allow the wireless users to access the external captive portal URL without being blocked by the firewall policy. Option A is false because enabling NAT in the firewall policy with the ID 13 will not affect the redirection to the external captive portal URL, but rather the source IP address of the wireless traffic. Option C is false because enabling the captive-portal-exempt option in the firewall policy with the ID 12 will bypass the captive portal authentication for the wireless users, which is not the desired outcome. Option D is false because removing the guest.portal user group in the firewall policy with the ID 12 will prevent the wireless users from being authenticated by FortiGate, which is required for accessing the external captive portal.
Which two statements about MAC address quarantine by redirect mode are true? (Choose two)
Answer : B, D
According to the FortiGate Administration Guide, ''MAC address quarantine by redirect mode allows you to quarantine devices by adding their MAC addresses to a firewall address group called Quarantined Devices. The quarantined devices are kept in their current VLANs, but their traffic is redirected to a quarantine portal.'' Therefore, options B and D are true because they describe the statements about MAC address quarantine by redirect mode. Option A is false because the quarantined device is not moved to the quarantine VLAN, but rather kept in the current VLAN. Option C is false because redirect mode is not the default mode for MAC address quarantine, but rather an alternative mode that can be enabled by setting mac-quarantine-mode to redirect.
: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiap/7.0.0/configuration-guide/734537/radius-authenticated-dynamic-vlan-allocation : https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/7.0.0/administration-guide/734537/mac-address-quarantine