Fortinet NSE6_FSW-7.2 Fortinet NSE 6 - FortiSwitch 7.2 Exam Practice Test
How is traffic routed on FortiSwitch?
Answer : D
Layer 3 routing can be configured on FortiSwitch, while managed by FortiGate (D): FortiSwitch, when managed by FortiGate, supports Layer 3 routing capabilities. This allows for routing between VLANs directly on the switch, enhancing network efficiency by reducing the need to pass traffic through higher network layers for inter-VLAN communication. This configuration enables more sophisticated network setups and efficient routing directly at the switch level.
Which drop policy mode, if assigned to a congested port, will drop incoming packets until there is no congestion on the egress port?
Answer : A
Tail-drop mode is a congestion management technique used in network devices, including FortiSwitches, to handle congestion on network ports:
Tail-Drop Mode (A):
Behavior: When a queue reaches its maximum capacity on a congested port, tail-drop mode simply drops any incoming packets that arrive after the buffer is full. This continues until the congestion is alleviated and there is space in the queue to accommodate new packets.
Application: This is a straightforward approach used when the device's buffer allocated to the port becomes full due to sustained high traffic, preventing buffer overflow and maintaining system stability.
Refer to the exhibits.
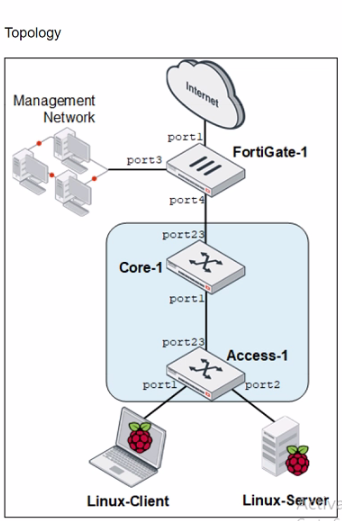
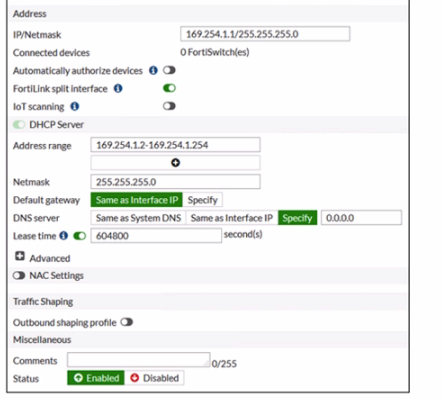
You are asked to ensure that managed FortiSwitch devices are reachable by other devices, such as SNMP and other management tools across your network.
Which setting must you configure to ensure traffic from other devices in the network reaches FortiSwitch?
Answer : B
Which statement about 802.1X security profiles using MAC-based authentication mode is true?
Answer : B
Pag 232, FortiSwitch_7.2_Study_Guide-Online 'However, if you want to authenticate each device behind a port, and optionally, grant each device a different access level based on the credentials provided, then MAC-based is required.'
Which two rules used by MSTP are similar to rules used by other STP methods? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, C
'MSTP is based on RSTP', so the same port role election and the same root bridge selection. Reference: FortiSwitch 7.2 Study Guide, page 187
Refer to the exhibit.
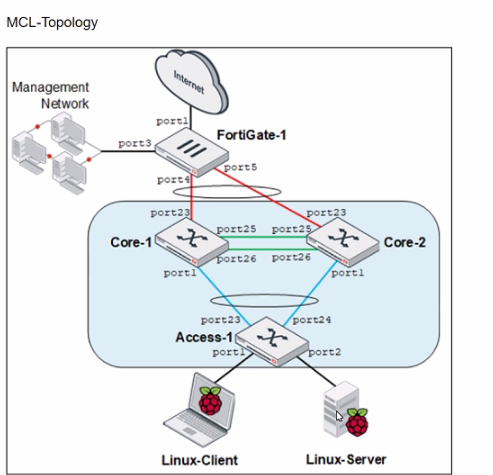
Core-1 and Access-1 are managed and authorized by FortiGate-1. which uses port4 as the FortiLink interface. After FortiGate authorizes and manages Core-2. Port1 status becomes STP discarding.
Why is port1 in the discarding state?
Answer : B
The STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) discarding state on port1 of Core-2, after Core-1 and Access-1 are managed and authorized by FortiGate-1, is likely due to the lack of an MCLAG (Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation Group) configuration between Core-1 and Core-2. In typical network configurations involving STP and MCLAG, the absence of MCLAG can lead to STP blocking one of the redundant paths to prevent loops, which is a critical function of STP. Port1 on Core-2 being in a discarding state suggests that it has been identified as providing a redundant path that could potentially create a network loop, hence STP has placed this port in a blocking (discarding) state to maintain a loop-free topology.
Refer to the diagnostic output:
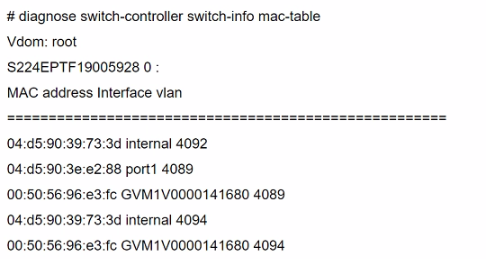
Two entries in the exhibit show that the same MAC address has been used in two different VLANs. Which MAC address is shown in the above output?
Answer : B
The MAC address '00:50:56:96:e3:fc' appearing in two different VLANs (4089 and 4094) in the diagnostic output indicates it is a MAC address associated with a device that supports traffic from multiple VLANs. Such a behavior is typical of network infrastructure devices like switches or routers, which are configured to allow traffic from various VLANs to pass through a single physical or logical interface. This is essential in network designs that utilize VLANs to segregate network traffic for different departments or use cases while using the same physical infrastructure.