Fortinet FCP_WCS_AD-7.4 FCP - AWS Cloud Security 7.4 Administrator Exam Practice Test
An administrator has been asked to deploy an active-passive (A-P) FortiGate cluster in the AWS cloud across two availability zones.
In addition to enhanced redundancy, which other major difference is there compared to deploying A-P high availability in the same availability zone?
Answer : D
Enhanced Redundancy:
Deploying an active-passive (A-P) FortiGate cluster across two availability zones (AZs) provides enhanced redundancy by ensuring that if one AZ fails, the other can take over, maintaining high availability and uptime.
IP Addressing and Subnetting:
One of the major differences when deploying across different AZs compared to the same AZ is that IP addressing and subnetting are not shared between the instances. Each AZ operates independently with its own set of subnets and IP addresses, which must be managed separately (Option D).
Other Options Analysis:
Option A is incorrect because the FortiGate devices in an A-P setup do not act as a single logical instance; they operate in a failover setup.
Option B is incorrect because secondary IP address configuration is used in both single AZ and multi-AZ deployments.
Option C is incorrect because the number of subnets required is typically more when deploying across multiple AZs for redundancy.
FortiGate HA Configuration Guide: FortiGate HA
An organization has created a VPC with two subnets and deployed a FortiGate-VM (VM04/c4.xlarge) in AWS.
The EC2 instance is initially configured with two Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs). The primary ENI is configured on the public subnet, and the secondary ENI is configured on the private subnet. To provide internet access for the FortiGate-VM, they now want to associate an EIP to its primary ENI, but the assignment is failing.
Which action would allow the EIP assignment to be successful?
Answer : C
Internet Gateway Requirement:
For an Elastic IP (EIP) to be assigned to an instance's primary ENI, the VPC must have an Internet Gateway (IGW) attached. The IGW enables the VPC to communicate with the internet, allowing the EIP to function properly (Option C).
Process of Assigning EIP:
Once the Internet Gateway is attached to the VPC, the EIP can be successfully assigned to the primary ENI of the FortiGate VM, providing it with internet access.
Other Options Analysis:
Option A is incorrect because the primary ENI is already in a public subnet.
Option B is not necessary and may not solve the issue without an attached Internet Gateway.
Option D is partially correct about the routing table but does not address the primary issue of needing an Internet Gateway.
A global organization with cloud networks deployed in several AWS regions wants to set up next-generation firewall (NGFW) protection using FortiGate Cloud-Native Firewall (CNF).
What are two deployment considerations for the organization? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, C
Regional Deployment:
For a global organization with cloud networks in multiple AWS regions, a separate FortiGate Cloud-Native Firewall (CNF) instance is required for each AWS region to provide localized protection and meet compliance requirements. This ensures that each region has its own dedicated NGFW protection tailored to its specific needs (Option B).
Multi-Account Association:
FortiGate CNF supports associating multiple AWS accounts with a single CNF instance. This feature is beneficial for organizations that operate in a multi-account setup, allowing centralized management and security policies across different accounts (Option C).
Other Options Analysis:
Option A is incorrect because AWS Firewall Manager is a different service and is not required to provision a CNF instance.
Option D is incorrect because a single CNF instance cannot protect multiple AWS regions due to regional isolation in AWS.
FortiGate CNF Documentation: FortiGate CNF
An AWS administrator is designing internet connectivity for an organization's virtual public cloud (VPC). The organization has web servers with private addresses that must be reachable from the internet. The web servers must be highly available.
Which two configurations can you use to ensure the web servers are highly available and reachable from the internet? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, D
Network Load Balancer:
Deploying a network load balancer ensures that incoming traffic is distributed across multiple web servers, providing high availability and redundancy. This setup helps in managing traffic efficiently and maintaining service uptime even if some servers fail (Option A).
Multiple Availability Zones:
Deploying web servers in multiple availability zones (AZs) enhances fault tolerance and availability. If one AZ goes down, servers in other AZs can continue to handle the traffic, ensuring the web application remains accessible (Option D).
Other Options Analysis:
Option B is incorrect because NAT Gateways are used to provide internet access to instances in private subnets, not to make private addresses reachable from the internet.
Option C is not sufficient on its own for high availability. Adding a route to the default VPC route table forwarding traffic to the internet gateway makes the VPC internet-accessible but does not ensure high availability.
AWS High Availability and Fault Tolerance: AWS High Availability
What is a drawback of deploying a FortiWeb VM inside a virtual public cloud (VPC) compared to FortiWeb Cloud?
Answer : D
VPC-Scoped Protection:
When deploying a FortiWeb VM inside a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), the security and protection it offers are limited to the applications and traffic that pass through that specific VPC. This means that any applications outside this VPC will not benefit from the protection of FortiWeb VM (Option D).
Comparison with FortiWeb Cloud:
FortiWeb Cloud, being a cloud-native WAF-as-a-Service, can protect applications regardless of their VPC location, offering broader and more flexible protection capabilities.
Other Options Analysis:
Option A is incorrect because both FortiWeb VM and FortiWeb Cloud protect against OWASP Top 10 threats.
Option B is incorrect because FortiWeb VM does support zero-day protection.
Option C is incorrect as the performance of FortiWeb VM in applying advanced WAF protection is not inherently slower compared to FortiWeb Cloud.
FortiWeb Overview: FortiWeb
Refer to the exhibit.
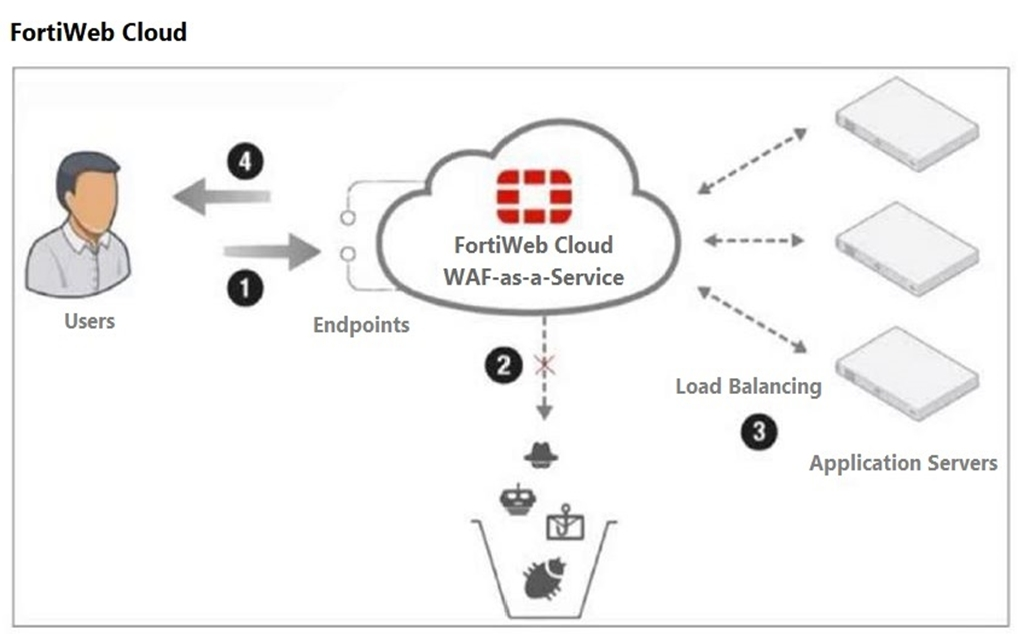
Which two statements are correct about traffic flow in FortiWeb Cloud? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, B
DNS Configuration:
For FortiWeb Cloud to effectively protect web applications, the DNS records for the application servers must be configured to point to FortiWeb Cloud. This ensures that all incoming traffic is routed through FortiWeb Cloud for inspection and protection (Option A).
Traffic Filtering:
FortiWeb Cloud provides robust protection by filtering incoming traffic to block the OWASP Top 10 attacks, zero-day threats, and other application layer attacks. This ensures the security and integrity of the web applications it protects (Option B).
Other Options Analysis:
Option C is incorrect because FortiWeb Cloud can protect application servers across different VPCs or regions, not just within the same VPC.
Option D is incorrect because step 2 does not require an AWS S3 bucket; it refers to the inspection and filtering of incoming traffic.
FortiWeb Cloud Overview: FortiWeb Cloud
Refer to the exhibit.
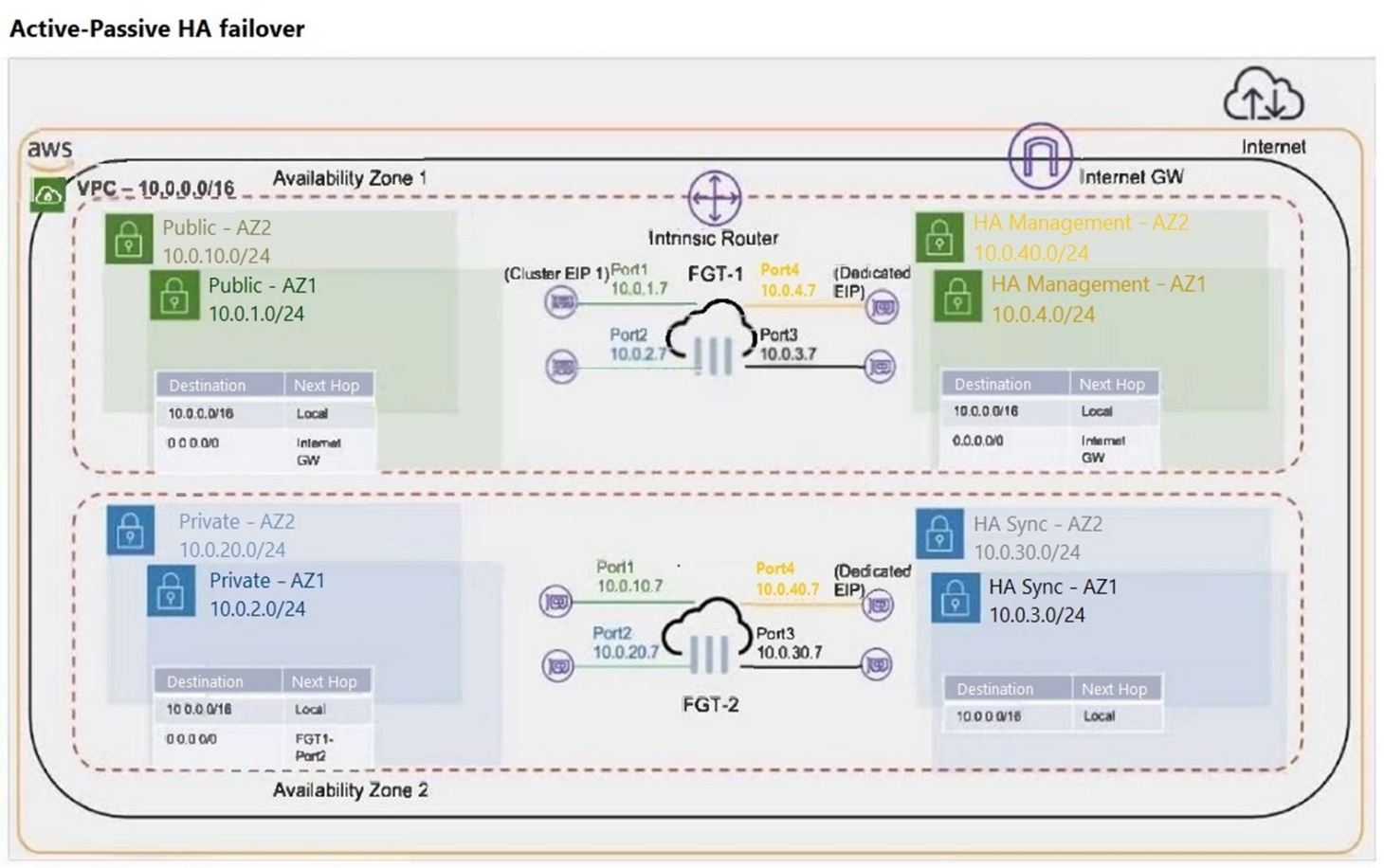
What occurs during a failover for an active-passive (A-P) cluster that is deployed in two different availability zones? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, B
Cluster Elastic IP Address (EIP) Movement:
During a failover in an active-passive (A-P) cluster, the Elastic IP (EIP) associated with the active FortiGate instance (FGT-1) needs to be moved to the passive instance (FGT-2), which becomes the new active instance. This ensures that the traffic directed to the EIP is now handled by FGT-2 (Option A).
Secondary IP Address Movement:
The secondary IP address on Port2 of the current active instance (FGT-1) is moved to the same port on the new active instance (FGT-2). This step is crucial to ensure seamless network traffic redirection and connectivity for the services relying on that IP address (Option B).
Other Options Analysis:
Option C is incorrect because the static route modification mentioned is not directly related to the failover process described.
Option D is incorrect because no additional route needs to be added to the HA Sync AZ2 subnet route table to forward traffic to the Internet Gateway during a failover.
FortiGate HA Configuration Guide: FortiGate HA