Ericsson ECP-206 Ericsson Certified Associate - IP Networking Exam Practice Test
What are two roles of the DHCP protocol in a network? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, B
Two roles of the DHCP protocol in a network are:
For IP destinations not found in the IS-IS Level 1 database, the Level 1 router must forward packets to the nearest Level 1-Level 2 router with which set?
What is the CLI command to obtain the software version in Ericsson Router 6000 products?
Review the exhibit.
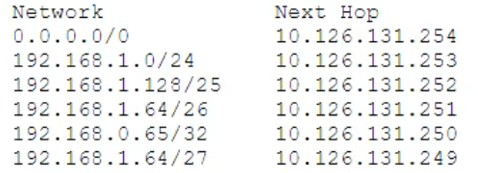
Given the routing table shown in the exhibit, what is the next-hop to reach the host 192.168.1.129?
Which two statements are true about link-state routing protocols? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, B
Link-state routing protocols are one of the two main classes of routing protocols used in packet switching networks for computer communications, the other being distance-vector routing protocols. Examples of link-state routing protocols include Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS). The basic concept of link-state routing is that every node constructs a map of the connectivity to the network, in the form of a graph, showing which nodes are connected to which other nodes. Each node then independently calculates the next best logical path from it to every possible destination in the network. Each collection of best paths will then form each node's routing table.
Two statements that are true about link-state routing protocols are:
The advertisement exchange is mainly triggered by a change in the network. Link-state routing protocols use a flooding mechanism to distribute information about the network topology to all routers in the same area or domain. This information is encapsulated in link-state packets (LSPs) or link-state advertisements (LSAs), which contain information about the router, its directly connected links, and the state of those links. LSPs or LSAs are sent only when there is a change in the topology, such as a link failure or recovery, or when a periodic refresh timer expires. This way, link-state routing protocols can quickly adapt to network changes and maintain an accurate and consistent view of the network.
Each router uses a reliable update mechanism to exchange topology information with its neighbors. Link-state routing protocols use a reliable update mechanism to ensure that all routers receive and acknowledge the LSPs or LSAs sent by their neighbors. This mechanism involves sending hello messages to establish and maintain adjacencies with neighbors, sending acknowledgment messages to confirm the receipt of LSPs or LSAs, and requesting missing or outdated LSPs or LSAs from neighbors. This mechanism ensures that all routers have a synchronized database of LSPs or LSAs, which is used to build a complete network connectivity map and to calculate the shortest path to destinations.