Dell EMC D-OME-OE-A-24 Dell OpenManage Operate Achievement Exam Practice Test
Refer to Exhibit:
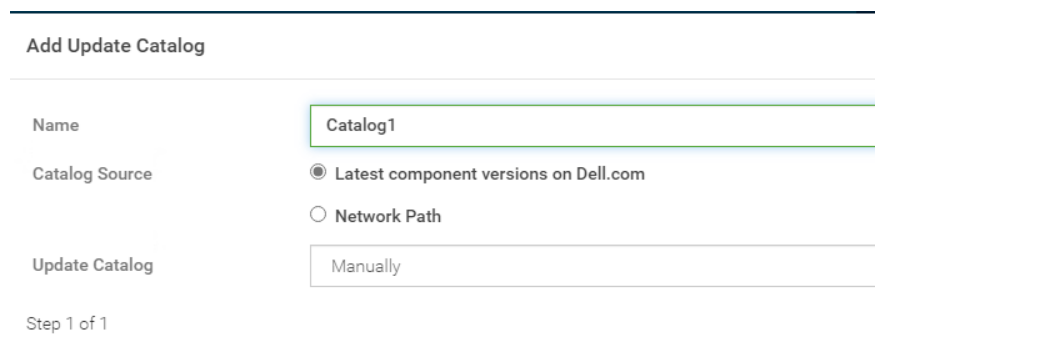
An OpenManage Enterprise environment contains both Dell EMC 13G and 14G PowerEdge servers and an online catalog that is configured as shown.
A Device Manager is tasked with creating a firmware baseline using Catalog1 for all the server infrastructure. During the task, they find that they are only able to select the 14G PowerEdge servers in
the environment.
What is causing the problem?
Answer : B
Understanding the Catalog Configuration: The online catalog, as shown in the exhibit, is configured to source the latest component versions from Dell.com. This catalog is named 'Catalog1'.
Identifying the Issue: The Device Manager is unable to select 13G PowerEdge servers when creating a firmware baseline using Catalog1. This indicates that the catalog lacks firmware for 13G servers.
Catalog Contents: Since Catalog1 is set to pull the latest component versions, it is likely that it only includes firmware for the most recent, supported server generations, which in this case appears to be the 14G PowerEdge servers.
Firmware Baseline Creation: Firmware baselines are created to standardize the firmware versions across the server infrastructure. If certain server generations are not included in the catalog, they cannot be selected for the baseline.
Reference to Dell OpenManage Documentation: Dell OpenManage documentation would typically explain how catalogs are associated with server generations and their firmware. It would state that if a catalog does not contain firmware for a particular generation, servers from that generation cannot be included in the baseline.
The exhibit provided context for the issue at hand, showing that Catalog1 is likely tailored for 14G servers, hence the absence of 13G server firmware. This aligns with standard practices for managing server firmware where catalogs are generation-specific to ensure compatibility and supportability.
Which page displays the history of all jobs and tasks in OpenManage Enterprise console?
Answer : A
In the OpenManage Enterprise console, the history of all jobs and tasks is displayed on the Monitor page. This page is designed to provide administrators with a comprehensive view of the operational status and history of tasks within the system.
Here's how you can view the job and task history:
Accessing the Monitor Page: Log into the OpenManage Enterprise console and navigate to the Monitor section.
Viewing Jobs and Tasks: Within the Monitor section, you will find various tabs and options that allow you to view the current status and history of all jobs and tasks that have been executed in the environment.
Job History Details: The job history will typically include details such as the job name, description, status, start time, end time, and any associated alerts or notifications.
This information is based on the standard layout and functionality of the OpenManage Enterprise console as described in the official Dell documentation and user guides. It is always recommended to refer to the latest OpenManage Enterprise documentation for the most current features and procedures.
How can OpenManage Enterprise be upgraded if the appliance does not have access to the Internet?
Answer : A
To upgrade OpenManage Enterprise without Internet access, you can use a Network File System (NFS) share that the appliance can access. Here's how to perform the upgrade:
Prepare NFS Share: Set up an NFS share on a server that the OpenManage Enterprise appliance can access. Ensure that the NFS share is properly configured with the necessary permissions.
Transfer to NFS Share: Copy the downloaded update packages to the NFS share.
Access OpenManage Enterprise GUI: Log into the OpenManage Enterprise appliance's graphical user interface (GUI).
Navigate to Update Section: Go to the update section within the GUI where you can manage appliance updates.
Specify NFS Share: Choose the option to upgrade from an NFS share and provide the path to the NFS share where the update packages are located.
Initiate Upgrade: Follow the prompts to initiate the upgrade process using the files from the NFS share.
=========================
When the maximum number of SNMP events are reached, how many events are placed in the archive?
Answer : A
The archiving process helps in managing the SNMP events efficiently by:
Ensuring that the most recent and relevant events are readily available for immediate viewing and action.
Storing older events in an archive for historical analysis and troubleshooting purposes.
Preventing the event log from becoming too large, which could potentially slow down the system or make it difficult to find specific events.
=========================
What advantage does the IPMI discovery protocol have over SNMP?
Answer : C
IPMI (Intelligent Platform Management Interface) is a set of computer interface specifications for an autonomous computer subsystem that provides management and monitoring capabilities independently of the host system's CPU, firmware, and operating system. One of the key advantages of IPMI over SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is its ability to monitor and manage various subsystem sensors within the hardware.
Moreover, IPMI operates independently of the operating system, which means it can function even if the server's OS fails or is unresponsive. This level of monitoring is crucial for maintaining system stability and preventing downtime due to hardware issues.
Dell EMC OpenManage SNMP Reference Guide1
Server Fault community discussions on Dell OpenManage and IPMI2
Spiceworks Community insights on Dell OpenManage monitoring3
=========================
Which are the minimum recommended hardware requirements to support up to 8,000 managed devices?
Answer : B
The minimum recommended hardware requirements to support up to 8,000 managed devices in Dell OpenManage Enterprise are 8 CPU cores and 32 GB memory. This configuration ensures that the system has sufficient resources to manage a large number of devices efficiently.
Here's a detailed explanation:
CPU Cores: The number of CPU cores directly impacts the ability of the OpenManage Enterprise appliance to process data and perform operations. With 8 CPU cores, the system can handle multiple tasks and processes concurrently, which is essential for managing thousands of devices.
Memory: 32 GB of memory provides the necessary buffer for the system to store and manage the information from all the managed devices. It allows for smooth operation and quick access to data, which is crucial when dealing with a large device ecosystem.
=========================
An OpenManage Enterprise administrator has been tasked to enforce server configuration policies on 2,000 servers using six different configuration profiles.
What is a valid method to create a compliance template?
Answer : C
To enforce server configuration policies on multiple servers using different configuration profiles, one valid method is to clone an existing template. Cloning allows administrators to take a pre-existing template that closely matches the desired configuration and make necessary adjustments to create a new compliance template. Here's how it can be done:
Access OpenManage Enterprise: Log into the OpenManage Enterprise console with administrative privileges.
Navigate to Templates: Go to the section where server templates are managed.
Select a Template: Choose an existing template that is closest to the desired configuration for the compliance policy.
Clone the Template: Use the option to clone the selected template. This will create a new template with the same configuration settings.
Modify the Template: Make any necessary changes to the cloned template to meet the specific requirements of the compliance policy.
Save the New Template: Save the newly created compliance template.
Apply the Template: Deploy the compliance template to the servers to enforce the configuration policies.